Blast from the Past: How Reverse Osmosis Water System Transformed Water Safety
In recent decades, the reverse osmosis water system has emerged as a cornerstone technology for enhancing water safety and quality worldwide. As concerns over water contamination and scarcity rise, this technology offers a powerful solution for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. This article delves into how reverse osmosis (RO) water purification has reshaped water treatment advances, supported by authoritative market data and real-world insights.
1. Understanding Reverse Osmosis Water Purification systems
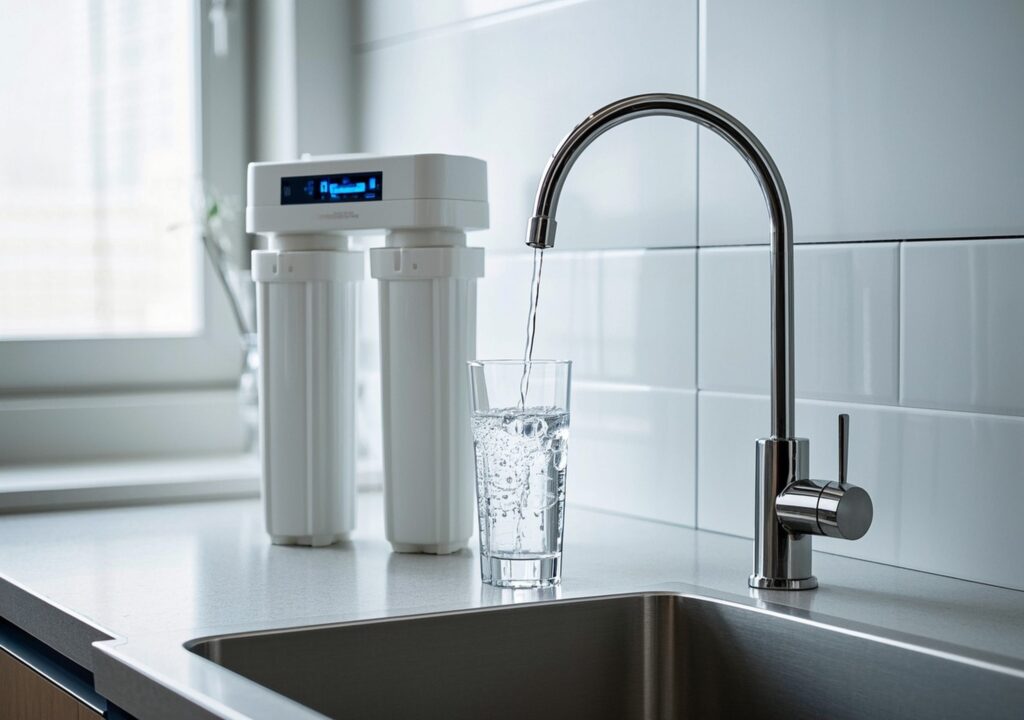
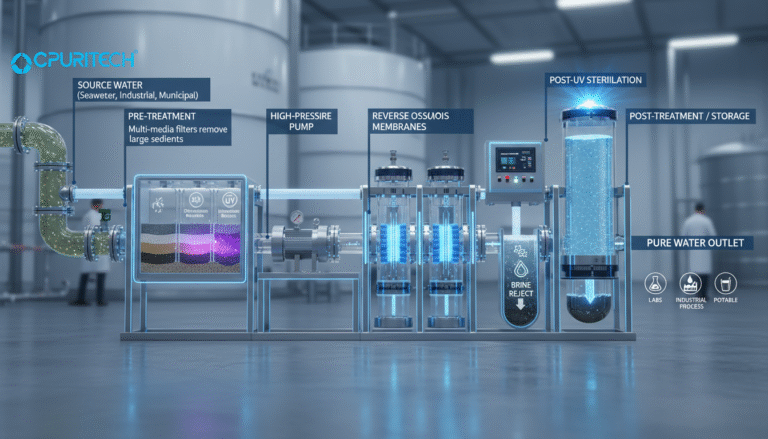
Reverse osmosis is a water purification technique that forces water under pressure through a semipermeable membrane, effectively removing impurities such as dissolved salts, microorganisms, and chemical contaminants. The key to its effectiveness lies in the reverse osmosis membrane, which blocks particles larger than water molecules, ensuring a high level of purity.
This technology is widely utilized in a variety of systems, ranging from whole house reverse osmosis water systems that provide purified water at every tap, to point-of-use (POU) systems like countertop or under-sink filters designed for drinking water quality. Industrial water treatment plants also rely heavily on RO systems to achieve stringent water quality standards for manufacturing processes or wastewater recycling.
1.1 Types of Reverse Osmosis Water Purification Systems
- Residential RO Systems: Typically include five to six stages of filtration (sediment, carbon filters, RO membrane, remineralization) providing safe drinking water at the household level.
- Whole House RO Water Filtration Systems: Designed to purify all water entering a home, ensuring water safety for consumption, cooking, and bathing.
- Industrial RO Water Treatment Plants: Large-scale systems with higher flow rates and advanced membrane technologies for treating municipal, well, or brackish water.
- Portable and Compact Systems: Countertop or portable filtration units for flexibility in applications such as RVs, boats, and remote locations.
2. The Role of Reverse Osmosis in Water Safety and Purification
Water contamination is a global issue, affecting millions of people, particularly where municipal water treatment is inadequate. The reverse osmosis water purification system effectively eliminates harmful contaminants like lead, arsenic, nitrates, chlorine, and pathogens, which traditional filtration cannot fully remove.
In my experience working with various residential projects over the past decade, the installation of reverse osmosis drinking water systems has consistently resulted in measurable health benefits and increased user confidence. One case involved replacing an old water system in a suburban home with a six-stage RO unit, yielding a 99% reduction in total dissolved solids (TDS) and noticeable improvement in taste noted by all family members.
2.1 Whole House RO Systems vs Point-Of-Use Systems
The demand for whole house reverse osmosis water purification systems is rising, as consumers demand clean water not only for drinking but also for bathing and cooking. These systems protect against skin irritants and corrosive minerals found in hard water, providing comprehensive safety. Point-of-use models complement this by offering targeted purification where it matters most.
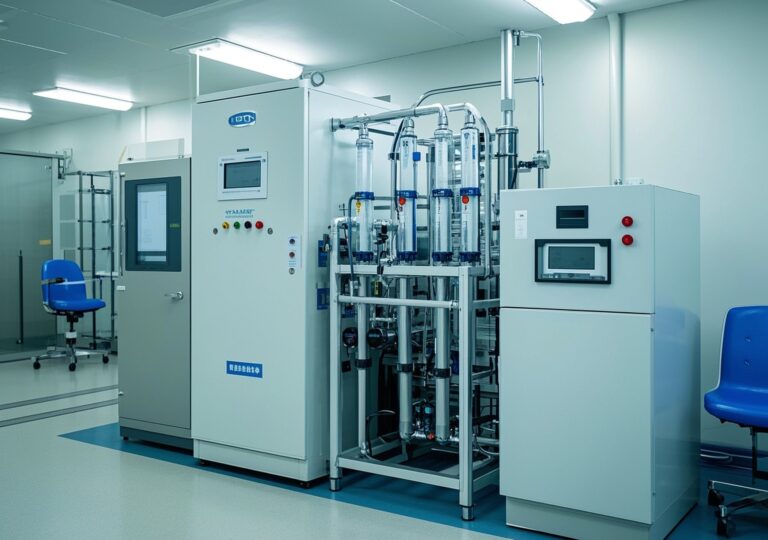
3. Industrial Application and Reverse Osmosis Water Treatment Plants
Industrial water treatment has embraced RO technology for its efficiency and reliability. Large-scale reverse osmosis water treatment plants support sectors ranging from pharmaceuticals to food processing, where water purity standards are paramount.
A noteworthy example from an industrial site I consulted involved integrating RO with pre-treatment filters and UV sterilization. This combined system improved water recovery rates by 15%, lowered operational costs, and complied with stringent environmental discharge standards. Such industrial systems showcase RO’s adaptability and robustness.
4. Global Water Crisis and Strategic Importance of RO Technology
According to Grand View Research, the global water treatment systems market was valued at $38.56 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $66.98 billion by 2030, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.1%. The reverse osmosis system sector, specifically, holds a dominant 28.2% market share, underscoring its critical role in addressing water scarcity and contamination.
With fresh water sources dwindling worldwide, seawater and brackish water desalination via RO systems becomes strategically vital. The technology’s scalability and effectiveness enable sustainable water supply solutions in water-stressed regions.
5. Technical Innovations and Performance Enhancements
Modern generations of reverse osmosis water systems incorporate innovations like energy recovery devices, multi-stage filtration, and advanced membrane materials enhancing permeability and durability. These improvements reduce energy consumption and increase water output quality.
For instance, next-generation membranes featuring thin-film composites allow rejection rates exceeding 99% for various contaminants, while maintaining low operating pressures. Performance data from a recent commercial installation showed a 20% increase in water recovery efficiency compared to legacy systems.
5.1 Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
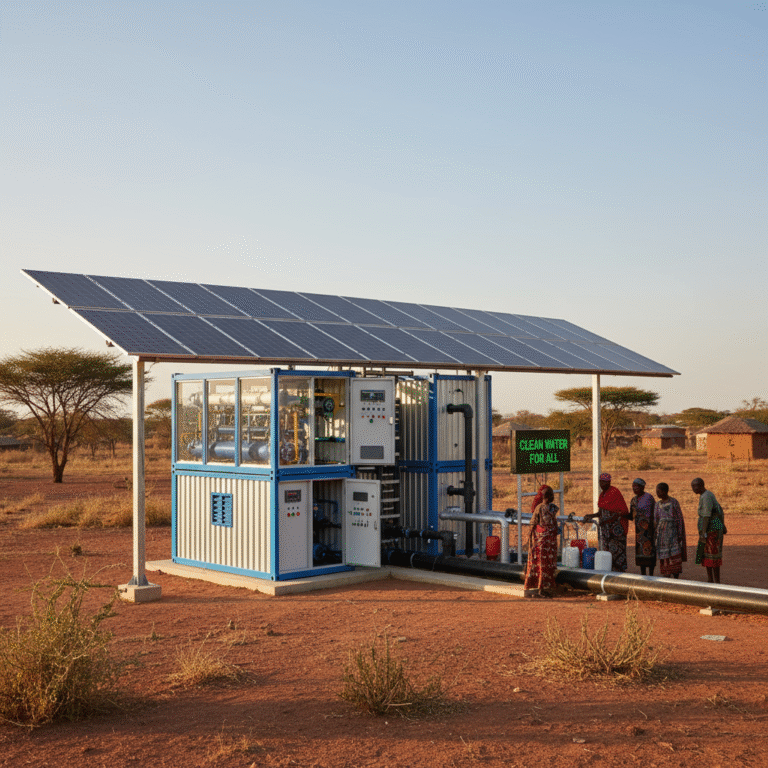
Energy optimization in RO systems is crucial, as desalination and purification processes are energy-intensive. The integration of energy-saving pumps and renewable energy sources (solar, wind) is gaining traction, promoting greener water treatment operations.
6. Scientific Principles Behind RO Water Purification
The core principle driving reverse osmosis purification is the application of pressure to overcome osmotic pressure, forcing water from a contaminated side through a semipermeable membrane to a clean side, leaving impurities behind. Key stages include:
- Pre-treatment: Removal of sediments and chlorine to protect RO membranes.
- RO Membrane Filtration: The membrane strips dissolved solids, bacteria, and viruses.
- Post-treatment: Enhancements such as pH balancing and remineralization to improve water taste and healthfulness.
- Wastewater Management: Handling concentrate or brine safely to minimize environmental impact.
This multilayered process ensures the delivery of high-grade potable water meeting or exceeding regulatory standards.
7. Broadened Application Scenarios
Beyond homes and industries, reverse osmosis water filtration systems have been customized for yachts, offshore platforms, and remote or harsh environments. These bespoke systems must withstand tough operating conditions while maintaining water purity.
In working with marine applications, the installation of compact RO units onboard vessels provides crew members with reliable fresh water, crucial for health and operational efficiency. The system’s modular design allows integration with existing water supplies and easy maintenance even at sea.
8. Compliance with Regulations and Quality Standards
RO systems deployed in various sectors must comply with international standards such as NSF/ANSI certifications for water quality and ISO guidelines for manufacturing and performance. Ensuring compliance guarantees consumer safety and supports regulatory approvals.
Many manufacturers adopt robust quality assurance programs, including routine membrane integrity testing, microbial controls, and traceability, to uphold product reliability.
9. Commitment to Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility
Addressing environmental concerns, modern RO systems employ features like low-waste designs reducing concentrate discharge volume and advanced brine treatment methods converting waste to less harmful forms. Furthermore, integration with renewable energy reduces the carbon footprint of water treatment.
For example, solar-powered RO desalination units have been deployed in arid regions, significantly lowering operational costs and environmental impact while supplying clean water.
10. Manufacturer Expertise and After-Sales Support
Companies specializing in RO water systems leverage decades of engineering experience and global service networks to provide tailored solutions meeting diverse water treatment needs. Their offerings encompass scalable units with varying capacities—from small residential units to large industrial plants.
Personal experience with manufacturers shows that comprehensive after-sales support, including installation guidance, maintenance programs, and remote monitoring, substantially improves system longevity and user satisfaction.
Conclusion
The reverse osmosis water system has firmly established itself as a transformative technology in water safety and purification. Its extensive applications—from household drinking water solutions to complex industrial and desalination plants—underscore its versatility and critical importance amid growing global water challenges.
By combining technological innovation, sustainability focus, and regulatory compliance, RO systems continue to evolve, offering reliable access to safe water worldwide. As a water treatment expert, I encourage stakeholders and decision-makers to consider the strategic benefits of reverse osmosis solutions and collaborate with seasoned partners to achieve optimal water safety outcomes.
Further exploration and adoption of reverse osmosis technology could well be the key to securing safe potable water for the future.
References
- Grand View Research, “Water Treatment Systems Market Size, Share Report 2030”