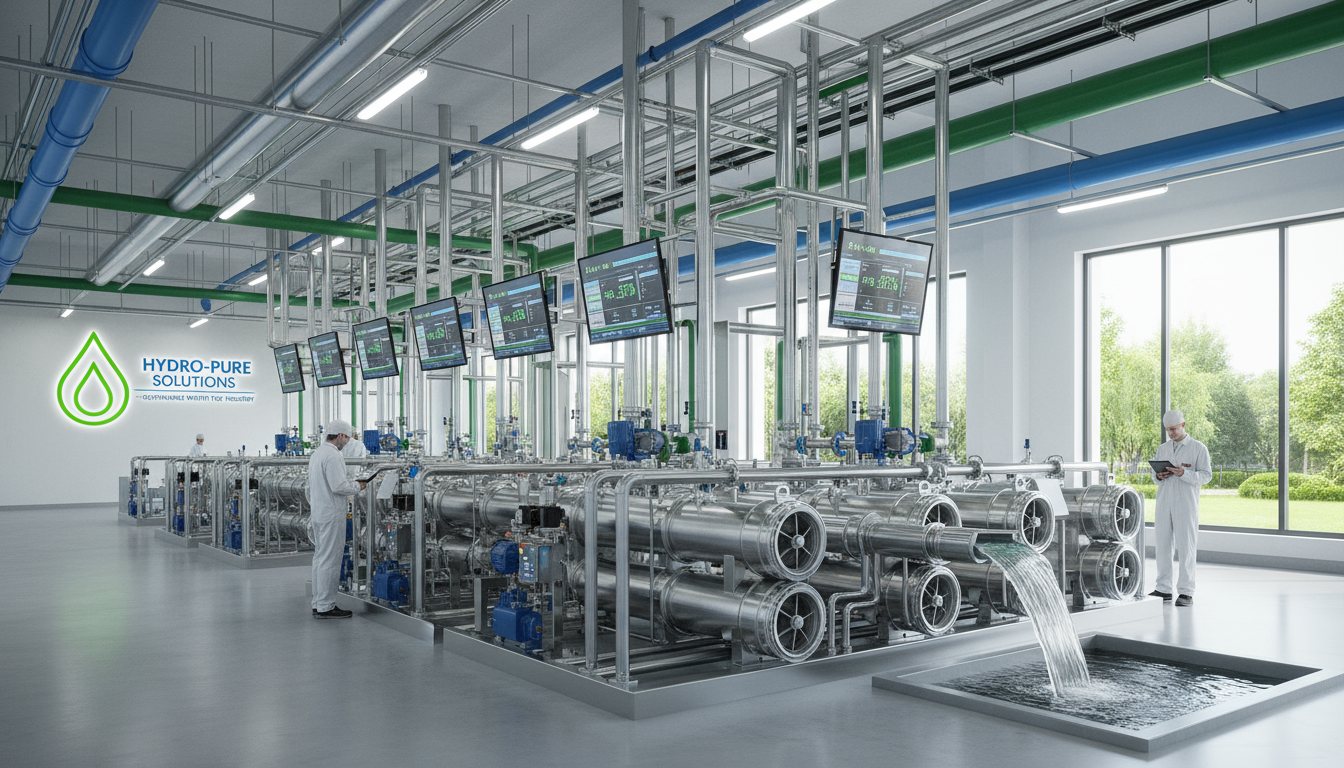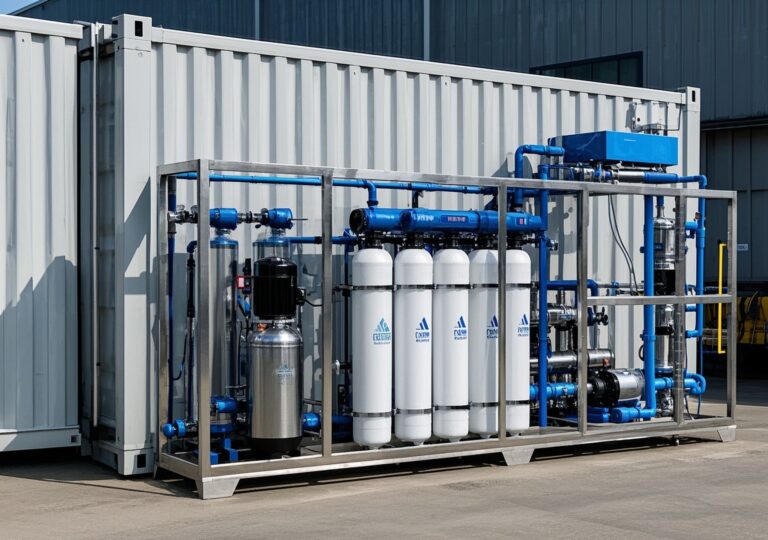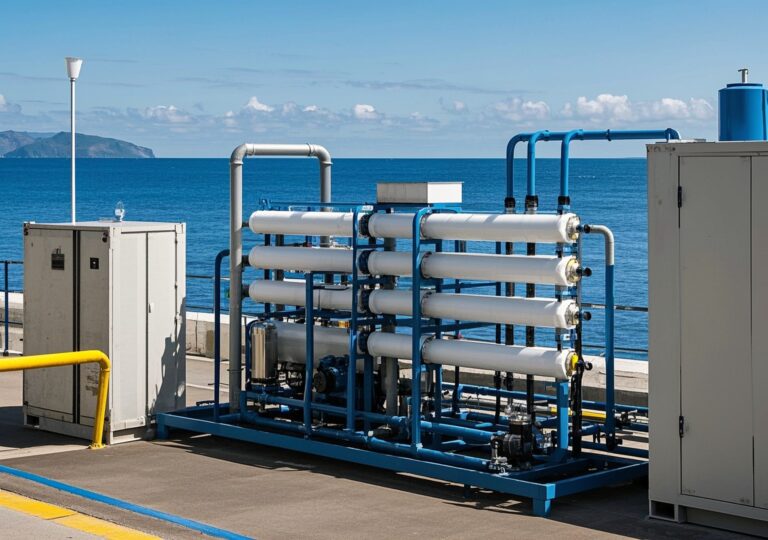
Introduction to Industrial Water Treatment Machinery
Water treatment plant machinery plays a vital role across various industrial sectors, ensuring safe, clean water supply and regulatory compliance. These advanced systems address the challenges posed by diverse water sources such as river water, groundwater, municipal supplies, well water, and process wastewater streams. Typical application industries include mining, food processing, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, laboratories, ultra-pure water production, boiler feedwater preparation, and municipal water treatment.
The primary goal of these machines is to remove contaminants, suspended solids, dissolved salts, organic pollutants, and pathogens, safeguarding both human health and equipment longevity. Their deployment enables industries to meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations and reduce water-related operational risks.
Technical Principles and Core Components
Modern water treatment plant machinery mainly relies on membrane separation technology, which has revolutionized industrial water purification processes. Membrane-based systems such as Reverse Osmosis (RO), Nanofiltration (NF), Ultrafiltration (UF), and Microfiltration (MF) operate by selectively allowing water molecules to pass through semi-permeable membranes while retaining contaminants. Among these, RO stands out with its exceptional capability of removing up to 99% of Total Dissolved Solids (TDS), including salts, heavy metals, and organic compounds (according to Netsolwater.com).
These systems consist of several critical parts:
- High-pressure pumps that drive feed water through membranes at adequate pressures.
- Membrane elements, typically made from polyamide thin-film composites, enabling selective separation.
- Automatic control units that monitor water quality parameters such as TDS, pressure, flow rate, and system integrity to optimize operational efficiency.
- Pre-treatment modules including sediment filters, activated carbon filters, and anti-scalants to protect membranes against fouling and extend lifetime.
- Post-treatment units, such as ultraviolet sterilizers or chemical dosing, to ensure microbiological safety and desired water chemistry.
In high-hygiene industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing, wetted parts such as pipes, valves, and membrane housings are constructed from certified materials compliant with stringent health and safety standards. For example, 316L stainless steel and FDA-grade polymers are prevalent choices, meeting certifications such as NSF/ANSI/CAN 61 in the US, EU Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 in Europe, and WHO Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) guidelines for pharmaceutical water systems.
Price Breakdown and Investment Analysis
Understanding the pricing structure of water treatment plant machinery is crucial for making informed investment decisions. The total cost typically includes:
- Base System Cost: This covers core equipment such as pumps, membranes, control systems, and piping. Variations arise depending on capacity, membrane type, and automation level.
- Optional Modules: Pre-treatment (e.g., advanced filtration), post-treatment (UV sterilization, chemical dosing), and enhanced control features might be added depending on specific water quality requirements.
- Installation and Commissioning: Engineering, civil works, and integration with existing infrastructure contribute a notable portion to upfront expenses.
- Operating and Maintenance Costs: Include energy consumption (notably for high-pressure pumps), membrane replacement intervals, chemical usage, and periodic system checks.
From my experience in industrial projects, investing in robust pre-treatment significantly reduces membrane fouling, increasing system uptime and lowering maintenance costs. For instance, a mining operation I consulted reduced membrane replacements by 30% annually by incorporating advanced sand filtration and anti-scalants without major upfront cost increases.
While initial capital expenditure may seem substantial, the long-term return on investment (ROI) is enhanced by lower water loss, improved product quality, compliance with discharge regulations, and potential reuse of treated water within the plant.
Performance Specifications and Quality Assurance
Key performance indicators (KPIs) for industrial water treatment equipment include:
- TDS Removal Efficiency: Typically 98-99% for RO membranes, effectively reducing total dissolved solids to acceptable limits.
- Flow Capacity: Scalable from small laboratory units producing a few cubic meters per day to large-scale plants handling thousands of cubic meters daily.
- Energy Consumption: Advanced designs consume approximately 0.14 to 1 kWh/m³ for brackish water, with seawater desalination requiring higher energy which can be optimized below 3 kWh/m³ using energy recovery technologies (based on data from Netsolwater.com and Cruise RO Water).
- Material Standards: Components contacting treated water comply with NSF/ANSI 61, FDA 21 CFR parts 170-199 (USA), EU 1935/2004, and WHO GMP guidelines to ensure safety and durability.
Quality assurance processes include rigorous material testing, membrane integrity checks before commissioning, and adherence to ISO/IEC quality management and environmental standards.
Global Market Insights and Application Scenarios
The global industrial water treatment market is witnessing steady growth, estimated at approximately USD 46.13 billion in 2024 with a projected CAGR of 5.1% through 2033 (Grand View Research). The Asia-Pacific region leads with over 38% market share and fastest growth, fueled by industrialization, urbanization, and stricter environmental policies.
Industries like semiconductors, pharmaceuticals, power generation, and food & beverage act as key demand drivers due to their need for ultra-pure water and tight effluent control. Semiconductor manufacturing, for instance, demands water with extremely low ionic content, while pharmaceutical processes require water adhering to WHO GMP standards.
Environmental regulations regarding wastewater discharge have become increasingly stringent globally. For example, the US EPA’s Effluent Limitation Guidelines and China’s GB8978 standard set pollutant concentration thresholds that industrial facilities must meet before discharge or reuse. Such tightening regulations significantly boost demand for advanced water treatment plant machinery capable of heavy metal, Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD), and ammonia nitrogen removal.
In the mining industry, where water reuse and zero liquid discharge (ZLD) strategies are increasingly adopted, customized treatment solutions reduce environmental impact and operational costs. In food processing and pharmaceuticals, certified sanitary materials and validated process controls are essential to prevent contamination and safeguard product quality.
Selected Industry Case Studies and Practical Insights
In my work with a pharmaceutical manufacturer, implementing a dual-stage RO system paired with UV disinfection brought TDS levels down from 500 ppm to below 10 ppm, consistently meeting WHO GMP standards. Over 2 years, the plant realized a 15% reduction in water procurement costs by recycling treated rinse water, and membrane lifespan extended by proactive online monitoring and cleaning cycles.
For a mid-size food processing facility, integrating NF membranes with automated control reduced organic contamination by 90%, improving product shelf life and reducing chemical cleaning downtime by 25%. Compliance with FDA 21 CFR and NSF/ANSI 61 standards for all contact materials ensured regulatory approvals and consumer safety.
A mining plant upgrade replacing traditional ion exchange units with RO-based systems cut energy consumption from an estimated 7 kWh/m³ to under 1 kWh/m³, leveraging modern pressure pumps and energy recovery devices. This upgrade delivered substantial savings on electricity bills and lowered carbon footprint, aligning with the company’s sustainability goals.
Customization Options and Comprehensive Service Support
Each industrial water treatment project demands a tailored engineering approach. Common customization options include:
- Pre-treatment systems adapted to feed water characteristics (e.g., hardness, turbidity).
- Post-treatment modules to achieve specific water chemistry targets or disinfection assurance.
- Advanced automation tailoring, with remote monitoring, predictive maintenance alerts, and integration with plant management systems.
- Modular construction facilitating phased upgrades and scalability.
Reliable installation and commissioning services, supported by trained technicians, ensure smooth project execution. Moreover, manufacturer-backed maintenance contracts, on-site troubleshooting, and supply of genuine replacement parts safeguard long-term performance.
Manufacturers’ Expertise and Collaboration Benefits
When selecting water treatment plant machinery, partnering with manufacturers possessing strong technical expertise, international certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, ISO 14001), and proven track records is essential. Such partners provide:
- Innovative R&D capabilities to stay ahead of evolving regulations and industry demands.
- Comprehensive documentation to support regulatory approvals.
- After-sales support networks facilitating spare parts availability and rapid response.
- Consultancy on designing water management strategies maximizing operational and environmental benefits.
From my observations, collaborative design processes involving client operations, water quality experts, and equipment engineers tend to yield solutions with superior reliability and cost efficiency.
Summary and Investment Recommendations
Water treatment plant machinery represents a critical asset in managing industrial water resources responsibly and sustainably. Cutting-edge membrane technologies combined with intelligent automation provide excellent contaminant removal, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
Investors should prioritize:
- Ensuring material and component certifications meet hygiene and environmental standards corresponding to target industry requirements.
- Allocating resources for comprehensive pre-treatment to extend equipment lifespan and reduce operational costs.
- Evaluating total cost of ownership rather than upfront capital alone, considering energy use, maintenance, and potential water reuse benefits.
- Partnering with experienced manufacturers offering robust service support to mitigate project risks.
With the global industrial water treatment market expanding driven by regulatory pressure and industrial demand, investing in efficient, adaptable equipment delivers both environmental and economic advantages.
References to Authoritative Data
Based on:
– NSF/ANSI/CAN 61: Drinking Water System Components – Health Effects (2024 revision)
– U.S. FDA 21 CFR parts 170-199 Food Contact Surface Materials
– EU Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 on Food Contact Materials
– WHO Good Manufacturing Practices for Pharmaceutical Water
– Netsolwater.com and Cruise RO Water on Membrane Efficiency and Energy Use
– Grand View Research and Data Insights Market Reports on Industrial Water Treatment Market Size and Trends
– US EPA Effluent Limitations Guidelines and Standards (ELGs)
– China Ministry of Ecology and Environment GB8978 Integrated Wastewater Standard
– Industry case studies and project experience synthesized through professional consulting practice





