Ensuring access to clean and safe drinking water remains one of the most critical challenges faced worldwide today. With global water consumption increasing at more than twice the population growth rate over the past century, countless regions are now perched on the brink of sustainable water resource limits. This pressure is especially severe in arid and water-scarce zones, where reliable water treatment and purification technologies have become indispensable to public health and economic development.
Among these technologies, the reverse osmosis water treatment system has distinguished itself by effectively removing a broad spectrum of contaminants and improving water quality for residential, commercial, and industrial use. In regions like Sub-Saharan Africa, identified as the world’s most water-insecure area, access to safely managed drinking water remains alarmingly low, affecting hundreds of millions of people. Deploying advanced water treatment solutions is not just a technical imperative but a moral necessity.
In my years of experience overseeing water projects, including collaborative efforts in arid regions, I’ve witnessed the tangible benefits reverse osmosis systems bring—transforming brackish or contaminated sources into potable water that meets and often exceeds stringent global health standards. This article explores the role of reverse osmosis technologies in securing safe water supplies, analyzes the pressing water resource challenges they address, and highlights customized solutions that can be adapted worldwide.
Understanding Reverse Osmosis and Its Role in Water Treatment

Reverse osmosis (RO) is a membrane-based water purification process that applies pressure to force water through a semipermeable membrane, filtering out dissolved salts, microbes, organic molecules, and other impurities. The technology stands out for its capacity to significantly reduce total dissolved solids (TDS), heavy metals, pathogens, and chemical contaminants, providing water quality suitable for drinking and sensitive industrial applications.
Modern RO systems often integrate pretreatment methods such as sand filtration, activated carbon filters, and water softeners to optimize membrane lifespan and efficiency. Post-treatment stages might include ultraviolet disinfection or remineralization to ensure water complies with international drinking standards. The adaptability of RO technology allows it to treat a wide variety of source waters, from seawater desalination to brackish groundwater and municipal supply augmentation.
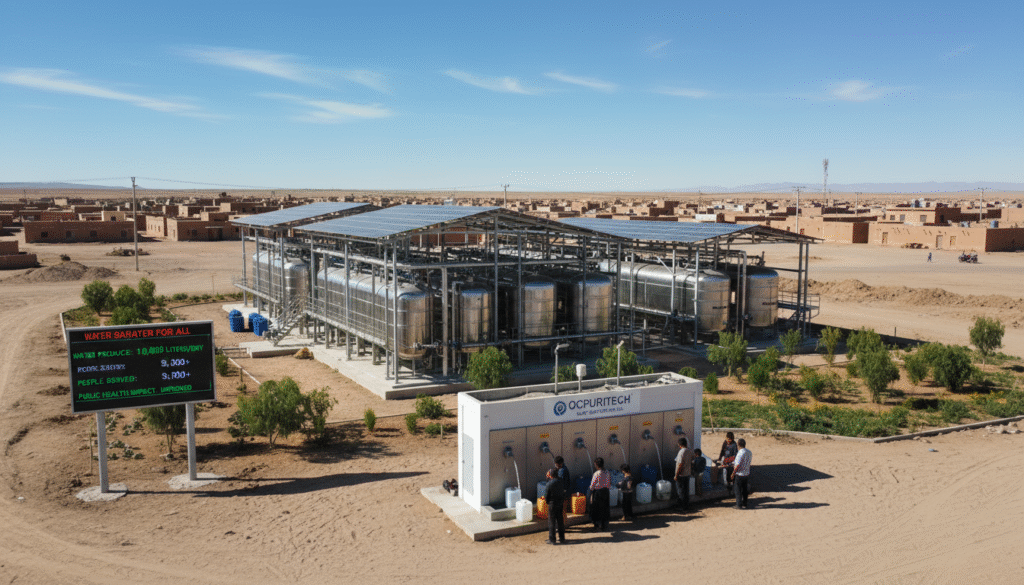
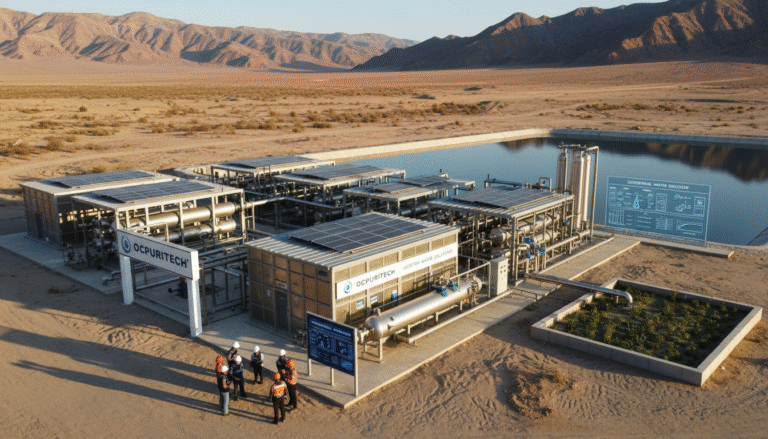
In my engagement with projects deploying RO systems, including those by Ocpuritech, a global leader with over 14 years of experience, we’ve consistently observed how combining remote control systems and integrated pretreatment can dramatically improve operational efficiency and water quality even in harsh environments. These solutions are pivotal in underserved markets such as Southeast Asia, Africa, and South America, where water quality challenges are acute.
The key advantages of reverse osmosis systems include:
- Removal of up to 99% of dissolved salts and contaminants.
- Reduction of bacteria, viruses, and protozoa.
- Versatility to treat various water types including seawater and brackish water.
- Compact footprint suited for diverse deployment scales.
- Integration capability with monitoring and remote control technology.
Water Scarcity Challenges Driving Demand for RO Systems

Water scarcity is on the rise globally, and the issue is most critical in regions like Sub-Saharan Africa, where every country has been rated as water insecure. Approximately 869 million people lack access to safely managed drinking water. Even with population growth nearing 20% in recent years, improvements in water service access have been marginal, underscoring the dire need for technological interventions.
The demographic surge and economic development intensify pressure on finite freshwater resources. According to studies, by 2025 nearly 1.8 billion people will live in areas facing “absolute” water scarcity, defined as less than 500 cubic meters of water per capita annually. This reality necessitates efficient water treatment systems that maximize resource use and deliver safe drinking water even under stringent supply constraints.
In the projects I have managed in arid zones, integrating reverse osmosis technology has proven essential to overcoming geographical and climatic limitations. For example, in a recent initiative providing safe drinking water to a rural community dependent on brackish groundwater, RO systems equipped with remote monitoring allowed for continuous quality assurance and maintenance, ensuring compliance with stringent health guidelines while keeping operational costs manageable.
Such water purification technologies also help mitigate the impact of climate variability on water security, enabling regions with limited natural freshwater reserves to achieve sustainable development goals and reduce disease burden linked to unsafe water consumption.
Adhering to Drinking Water Standards with RO Technology
Globally recognized drinking water standards, such as those established by the World Health Organization, provide essential frameworks to safeguard public health. These guidelines address both chemical and microbial parameters and serve as benchmarks for water treatment performance.
RO water treatment systems are designed to meet or exceed these international standards by efficiently removing contaminants that often evade conventional treatment methods. The systems are calibrated to lower chemical residues, heavy metals, and pathogens to levels well below the limits prescribed.
A comprehensive water treatment process typically includes:
- Pretreatment for sediment and chlorine removal
- Softening to reduce scaling potential
- Reverse osmosis membrane filtration
- Post-treatment disinfection and adjustment
- Continuous monitoring of water quality parameters
In my professional experience, tailoring the pretreatment and control systems based on water source characteristics and target quality standards proves critical. For instance, in a drinking water project in Southeast Asia, adjusting pretreatment to reduce turbidity saved costs and prolonged membrane life significantly, ensuring consistent compliance with WHO guidelines while maximizing operational sustainability.
Furthermore, certifications like ISO 11133 for microbial testing and ISO 9308-1 for E. coli enumeration help validate the safety and reliability of RO-treated water, giving consumers and stakeholders confidence in the system’s performance.
Custom Solutions and Engineering Design for Diverse Applications
Each water treatment application demands a tailored solution influenced by factors like scale, source water quality, budget, and local environmental conditions. Reverse osmosis systems can be adapted to serve small communities, commercial enterprises, or large-scale industrial plants.
Good engineering design incorporates multiple stages, including pretreatment with sand filters, carbon filters, and softeners; the RO membrane unit; and post-treatment modules. Monitoring and control systems enable real-time performance tracking and fault detection, reducing downtime and maintenance expenses.
I have overseen the design and deployment of remote-controlled RO systems leveraging smart sensors and automation, which have proved invaluable in remote or resource-limited settings. These systems allow operators to gather operational data, optimize parameters, and schedule maintenance proactively, ensuring a longer membrane lifespan and better water quality.
Quality assurance protocols include:
- Robust pretreatment to minimize fouling
- High-quality membrane selection tailored to feed water
- Automated flushing and cleaning procedures
- Integrated water quality sensors for continuous assessment
- Compliance verification through periodic lab testing
For example, a drinking water treatment facility serving an urban community in South America employed this integrated approach and reported up to 40% reductions in operational costs compared to conventional systems while delivering superior water quality.
Brand leaders like Ocpuritech continuously innovate in this domain, providing cost-effective, reliable systems manufactured in standardized factories and supported by a comprehensive spare parts supply chain. Their global footprint underscores a commitment to making clean water accessible everywhere.
Case Studies Demonstrating the Impact of Reverse Osmosis Systems
Throughout my career, I have been fortunate to lead and consult on projects utilizing reverse osmosis systems that have materially improved water security and public health outcomes. One illustrative case involved a semi-arid region community grappling with groundwater contamination and seasonal droughts.
By implementing a comprehensive RO water treatment plant with remote control capabilities and integrated pretreatment, the community achieved:
- Consistent production of potable water meeting WHO standards
- Reduction of waterborne illnesses by over 50% within the first year
- Enhanced water reliability during dry seasons
- Improved local economic activities dependent on safe water
In another project supporting bottle water production lines, integration of RO systems allowed for better control of water quality, reducing product recalls and elevating brand reputation. This also generated substantial water savings and minimized waste rejection rates by employing WaterSense certified units, demonstrating sustainable technology benefits.
These examples underscore the transformative impact that tailored reverse osmosis water treatment systems can have on water security, emphasizing the importance of expert design and ongoing technical support for sustainable results.
Conclusion: Securing Water Futures Through Advanced RO Technologies
In summary, the adoption of reverse osmosis water treatment technology represents a vital step towards addressing the growing water scarcity and contamination challenges worldwide. By combining advanced membrane filtration with intelligent engineering design, these systems ensure clean, safe water is accessible, even in the most resource-constrained settings.
Brands with proven experience, like Ocpuritech, provide comprehensive solutions that blend quality manufacturing, technical innovation, and global service networks. Whether for drinking water, agricultural, medical, or industrial uses, customized RO systems empower communities and businesses to meet stringent health standards and foster sustainable water use.
I encourage stakeholders in water-stressed regions to engage with water treatment experts to explore how reverse osmosis technologies can be tailored to their specific requirements. Together, we can make strides towards universal access to safe drinking water, protecting health and securing economic prosperity for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What contaminants does a reverse osmosis water treatment system remove?
RO systems remove dissolved salts, heavy metals, bacteria, viruses, protozoa, organic chemicals, and other impurities, greatly improving water quality.
Q2: How does RO compare to other water purification methods?
RO offers more comprehensive contaminant removal than conventional filtration or disinfection, making it highly effective for producing potable water from varied sources.
Q3: Is reverse osmosis suitable for seawater desalination?
Yes, RO is commonly used to desalinate seawater, producing fresh water by removing salts and other minerals effectively.
Q4: What are the maintenance requirements for RO systems?
Periodic membrane cleaning, pretreatment media replacement, and monitoring system checks are necessary to maintain efficiency and water quality.
Q5: Do reverse osmosis systems waste a lot of water?
Traditional RO systems generate reject water, but modern WaterSense certified units optimize efficiency to minimize waste, sometimes recovering a significant share of feed water.
Q6: Can RO systems be remotely monitored?
Yes, integrating remote control technology enables real-time monitoring, performance optimization, and proactive maintenance.
Q7: Are RO purified waters compliant with international drinking water standards?
Correctly designed and maintained RO systems can consistently meet WHO and other international guidelines for safe drinking water.
Q8: What kind of pretreatment is necessary before RO?
Pretreatment often includes sediment filtration, activated carbon, and water softening to protect membranes from fouling and chlorine damage.
Q9: Is reverse osmosis technology environmentally sustainable?
Advanced RO designs focus on reducing water waste and energy consumption, contributing to sustainable water management goals.
Q10: How do I select a reliable reverse osmosis system provider?
Choose suppliers with established expertise, quality certifications, and strong after-sales support, ensuring solutions tailored to your water quality and capacity needs.