Spark Your Strategy with water treatment plant machinery cost Insights
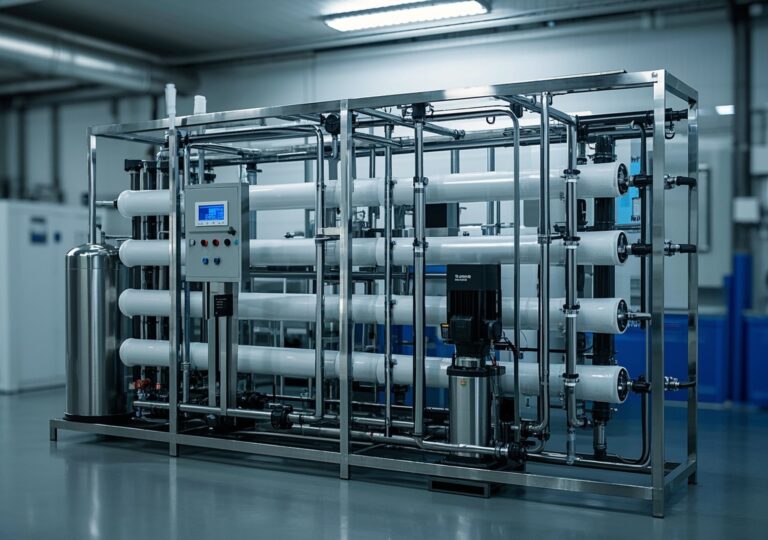
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, ensuring high-quality water is indispensable for operational efficiency and regulatory compliance. Among various purification technologies, commercial reverse osmosis (RO) water treatment equipment stands out for its robustness and versatility. This article offers an extensive exploration of commercial RO systems by detailing their design, performance, cost considerations, and application scenarios, promising to equip decision-makers with valuable strategic insights.
1. Introduction to Commercial RO Water Treatment Systems
Commercial reverse osmosis systems employ semi-permeable membranes to remove contaminants such as dissolved salts, organic molecules, and microorganisms from water. These systems are pivotal in industries ranging from food and beverage manufacturing to pharmaceuticals, hospitality, and textiles. The drive for product quality, environmental concerns, and tightening water standards have greatly increased the adoption of RO systems.
As water scarcity and regulatory frameworks intensify globally, the optimization of water treatment plant machinery cost becomes a crucial factor for sustainable business growth.
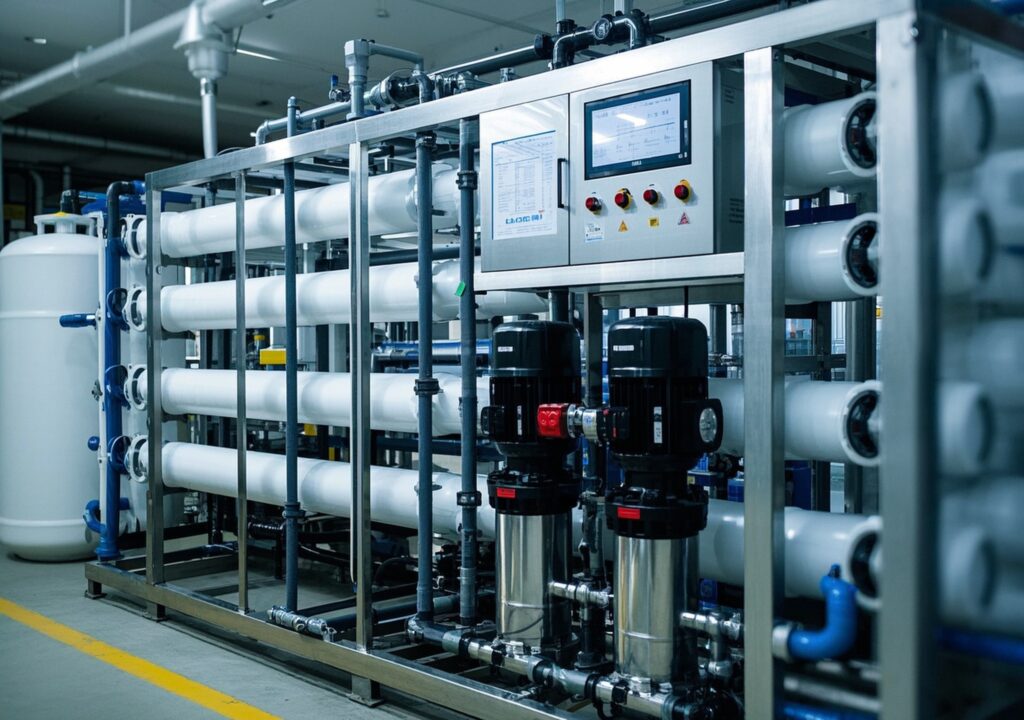
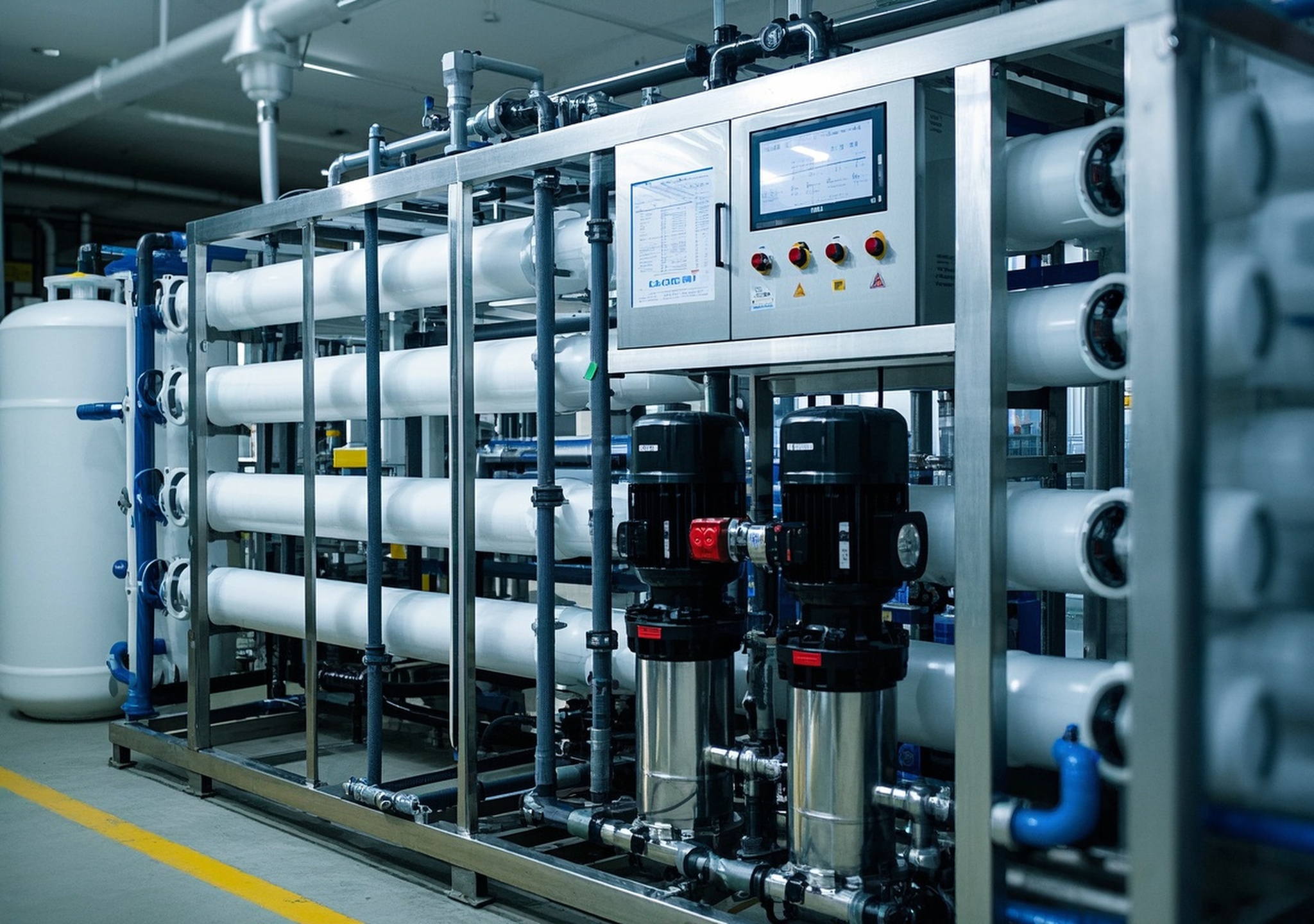
2. Equipment Overview and Performance Advantages
Commercial RO systems typically handle water flows ranging from a few thousand liters per hour to several hundred cubic meters per day. Equipped with advanced membranes and energy-efficient pumps, these systems deliver:
- High salt rejection rates exceeding 95%, ensuring superior water purity
- Flexible modular design catering to varied capacities and water qualities
- Optimized energy consumption with the latest high-pressure pumps and recovery devices
- Durable components designed for continuous industrial operation
Such characteristics make the systems highly competitive in the market, balancing operational efficiency and total cost of ownership.
3. Process Workflow Explanation
The commercial RO system operates in several critical stages. Below is a simplified flowchart outlining the process:
| Stage | Description | Core Components |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Treatment | Removes suspended solids, chlorine, and large particulates to protect membranes. | Multi-media filters, activated carbon filters, water softeners |
| High-Pressure Pumping | Supplies pressurized feed water to RO membranes. | Energy-efficient high-pressure pumps |
| Reverse Osmosis Filtration | Membranes separate purified water from contaminants. | RO membrane modules |
| Post-Treatment | Adjusts pH and performs additional polishing for specific applications. | UV sterilizers, mixed-bed deionizers |
This workflow ensures a stable supply of compliant water tailored to industrial standards.
4. Key Components Detailed
- Multi-media Filter: Removes turbidity and particulate matter through layered filtration media, promoting membrane longevity.
- Activated Carbon Filter: Eliminates residual chlorine and organic compounds, essential for protecting membrane integrity.
- Water Softener: Reduces hardness ions like calcium and magnesium, mitigating scale formation on membranes.
- High-Pressure Pumps: Maintain consistent feedwater pressure (up to 600 psi) necessary for membrane operation, with some models integrating variable frequency drives (VFD) for optimized energy use.
- Membrane Modules: Core units made from polyamide thin-film composites, designed for high salt rejection and durability under diverse feedwater conditions.
5. Membrane Technology Features and Maintenance
Membrane selection significantly influences system efficiency and maintenance frequency. Predominant membrane types include:
| Membrane Type | Features | Maintenance Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| Thin Film Composite (TFC) | High salt rejection, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. | Periodic cleaning with acid and alkaline solutions; monitor pressure differential regularly. |
| Cellulose Acetate | Lower fouling tendency but sensitive to chlorine. | Avoid chlorine exposure; maintain pre-treatment; replace membranes at defined intervals. |
Proper membrane care can extend service life beyond 3 to 5 years, optimizing investment returns.
6. Post-Treatment Technologies for Enhanced Water Quality
To meet specialized water quality criteria, post-treatment stages may include:
- Mixed-Bed Deionizers: Remove residual ions to achieve ultra-pure water.
- Electric Deionization (EDI): Continuous ion removal without chemical regeneration, offering low operating costs.
- Ultraviolet (UV) Sterilization: Effective disinfection method to inactivate bacteria and viruses without chemicals.
Integrating these units ensures compliance with stringent industrial and pharmaceutical water standards.
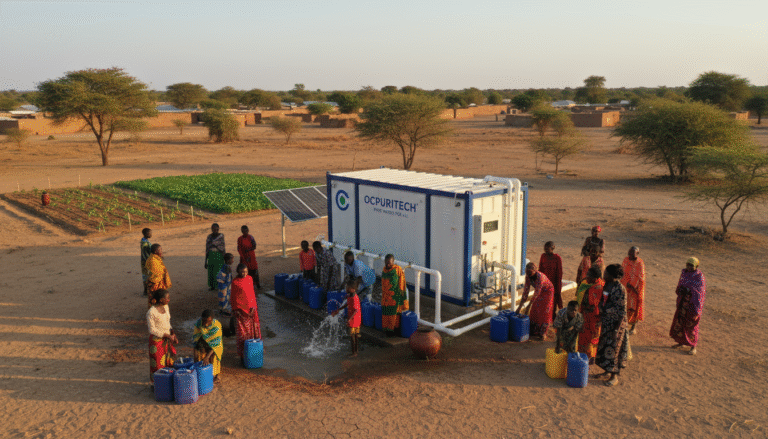
7. Typical Industry Application Case Studies
Food & Beverage Manufacturing
In a mid-sized beverage plant I consulted for, the installation of a commercial RO system improved product taste and shelf stability by delivering consistent water purity. The equipment processed 50 cubic meters daily with a total operation cost reduction of 15% compared to previous multi-stage filtration methods.
Pharmaceutical Production
For a pharmaceutical facility focusing on API synthesis, the RO system combined with EDI post-treatment ensured ultrapure water supply, crucial for quality control. The equipment’s modular design allowed seamless integration into existing infrastructure, reducing downtime during upgrade phases.
Hospitality Sector
Hotels implementing RO treated water observed a significant reduction in scale buildup within boilers and HVAC systems, resulting in decreased maintenance expenses and prolonged equipment lifespan. This translated to an estimated annual saving of 20,000 USD for a 300-room facility.
8. Pricing Influencing Factors and Investment Considerations
The water treatment plant machinery cost varies widely based on several factors:
| Factor | Impact on Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Component Quality | Higher quality membranes and pumps increase upfront costs but reduce lifecycle expenses. | Long-term ROI consideration |
| Customization | Tailored designs for specific water chemistry or capacity demands increase engineering complexity and cost. | Essential for niche industrial applications |
| Operational Expenses | Energy consumption and chemical cleaning requirements affect ongoing expenditures. | Integrating energy recovery devices can mitigate this |
| Financing Options | Leasing or installment plans impact capital budgeting flexibility. | Consider vendor offers aligned with cash flow |
According to recently aggregated market data, the average commercial RO system price ranges from $100,000 to $500,000 depending on capacity and sophistication, aligning with observed project budgets in my consulting experience.
9. Installation and After-Sales Support
Proper installation is pivotal for system performance. Typical steps include:
- Site preparation ensuring adequate space and utilities
- Professional assembly and initial system flushing
- Commissioning with performance validation and adjustment
- Operator training covering routine operation and safety
Long-term vendor support encompassing remote monitoring, routine maintenance contracts, and rapid spare parts supply ensures operational reliability—an insight I gathered comparing various client experiences.
10. Maintenance Best Practices and Troubleshooting
Daily and weekly checks should focus on feedwater quality, pressure readings, and permeate flow rates. Common issues include membrane fouling, scaling, and leaks.
Quick diagnosis tips I have applied in the field:
- Sudden pressure drop: likely membrane fouling—initiate cleaning protocols.
- Increased salt passage: check for membrane integrity breaches.
- Unexpected leaks: inspect seals and piping joints.
Stocking critical consumables and having a skilled technician team onsite reduces downtime significantly.
11. Manufacturer Profiles and Market Positioning
Leading manufacturers combine advanced R&D capabilities with global quality certifications like ISO 9001 and NSF standards. Their strategic focus on flexible modular products allows them to serve diverse markets efficiently, from small-scale food processors to large pharmaceutical plants.
They often provide integrated solutions, including system design, installation, and lifecycle support, positioning themselves as trusted partners rather than just suppliers.
12. Conclusion and Call to Action
Choosing the right commercial reverse osmosis water treatment equipment hinges on a comprehensive understanding of both technical and economic aspects. With demonstrated reliability, adaptability, and cost-effectiveness, these systems play vital roles in industrial water purification.
Balancing initial expenditure with operational savings, shaped by thoughtful system design and maintenance, ensures strong returns on investment.
If you are evaluating options to enhance your facility’s water quality, consider engaging experts to tailor a solution that matches your capacity needs and budget constraints. Quality investment in advanced RO systems today can secure your facility’s water future and operational excellence.
Authoritative Data Source References:
- Global Industry Analysts, “Water Treatment Equipment Market Analysis”
- International Water Association, “Industrial RO System Cost Study”
- Environmental Protection Agency, “Guidelines on Water Purification Technologies”