Zestful Journey: How a Reverse Osmosis Water System Boosted Our Quality
In the quest for reliable and efficient water purification, the reverse osmosis water system stands out as a cornerstone technology. Its capacity to provide clean, safe, and consistent water quality has revolutionized both residential and commercial water treatment applications. As global industrial demand for pure water surges, understanding the intricacies, benefits, and operational aspects of commercial reverse osmosis (RO) water treatment systems becomes essential. This extensive guide unveils the complex world of commercial RO equipment, backed by authoritative data and real-world insights, aiming to equip industry stakeholders and water treatment professionals with a detailed knowledge base.
1. Introduction: The Role of Reverse Osmosis in Modern Water Treatment
Reverse osmosis (RO) technology involves forcing water through semi-permeable membranes to remove dissolved solids, contaminants, and impurities, significantly enhancing water quality. Originating as a robust method for desalination, it now plays a fundamental role across diverse sectors such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, electronics manufacturing, and hospitality.
According to Grand View Research, reverse osmosis systems accounted for approximately 28.2% of the global water treatment system market revenue in 2023, highlighting its dominant market position. Industrial applications drive the expanding demand for commercial RO water treatment equipment, forecasting a market growth to $12.5 billion by 2025 with a CAGR of 8.5% through 2033 (Archive Market Research).
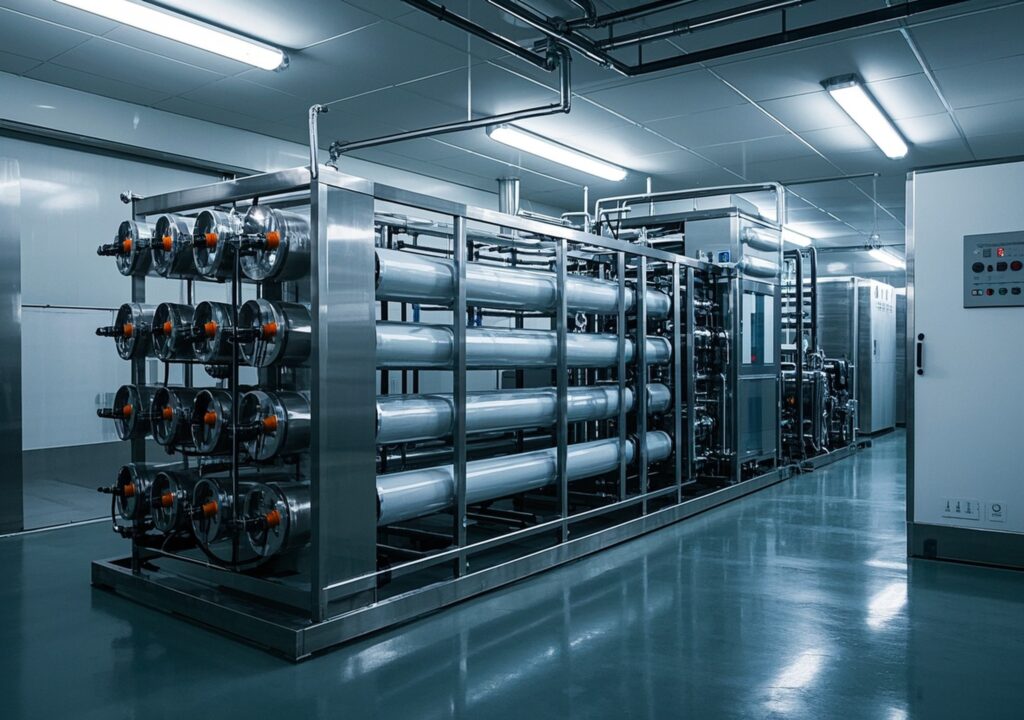
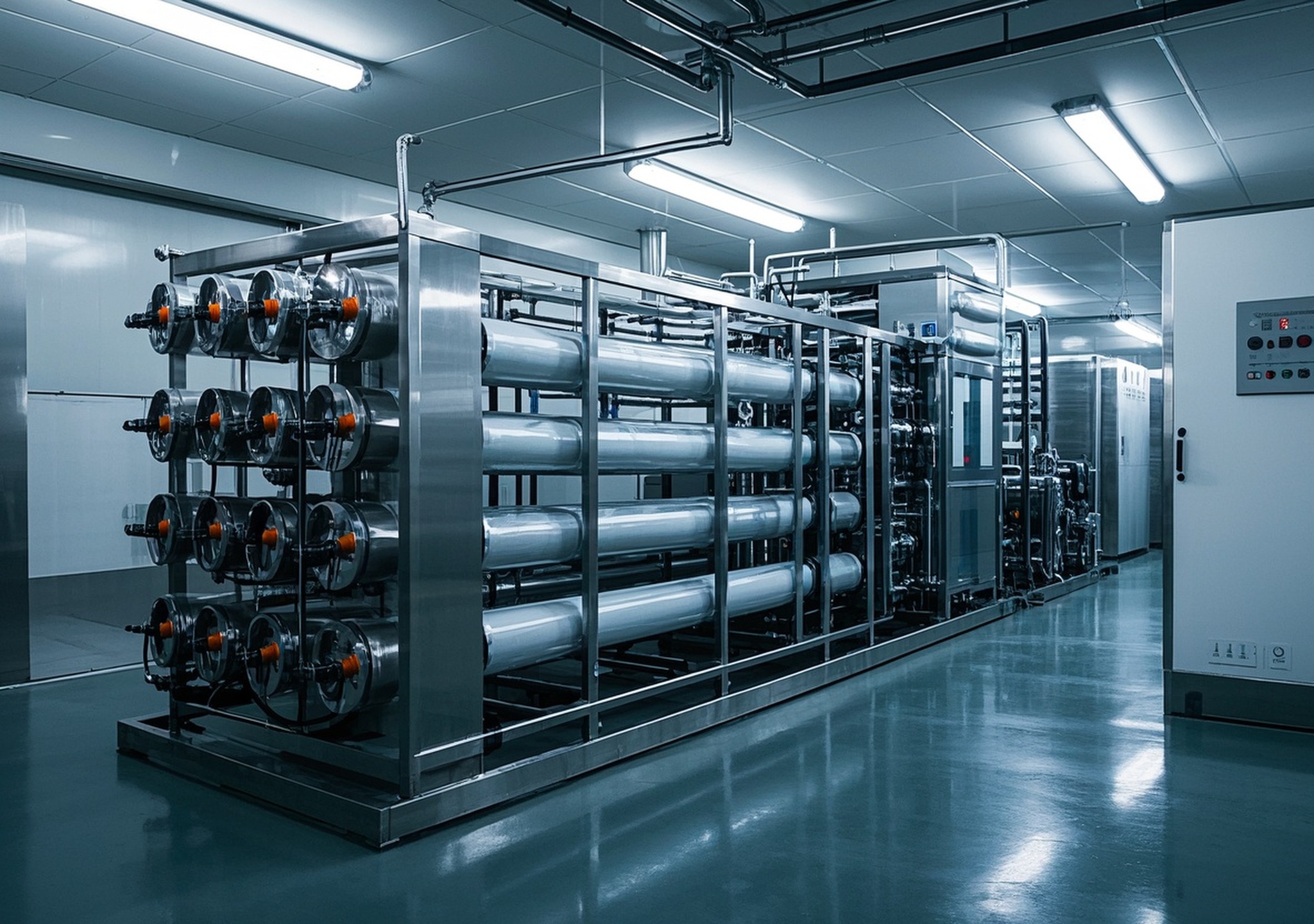
2. Overview and Performance Advantages of Commercial RO Water Treatment Equipment
Commercial reverse osmosis systems are designed to handle high flow rates and variable feed water qualities while ensuring consistent output purity. Key performance metrics include rejection rates typically above 95%, recovery rates between 50–85%, and the capability to process feed water with a wide range of Total Dissolved Solids (TDS).
Advanced commercial RO systems offer:
- Scalable capacity: Customizable flow rates from a few thousand gallons per day to millions, adaptable to various industrial requirements.
- Robust construction: High-grade materials and corrosion-resistant components for long service life under harsh conditions.
- Energy efficiency: Optimized pump and membrane designs lower energy consumption, decreasing operational costs.
- Automated operation and monitoring: PLC-controlled systems with sensors enable real-time water quality tracking and fault detection.
These systems deliver purified water conforming to industry standards for applications demanding ultra-pure water, thus ensuring process integrity and product quality.
3. Process Flow of Commercial Reverse Osmosis Systems
The commercial RO water purification process consists of several critical stages, each ensuring the removal of different contaminants and protection of the RO membranes.
| Stage | Description | Key Components |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Pre-treatment | Removal of suspended solids, chlorine, organics, and hardness minerals to protect membranes and reduce fouling. | Multimedia filters, activated carbon filters, water softeners |
| 2. High-pressure Pumping | Pressurizes pre-treated water to required operational pressures (typically 150-600 psi), critical for membrane performance. | High-pressure centrifugal or positive displacement pumps |
| 3. Reverse Osmosis Membrane Filtration | Water passes through semi-permeable membranes which remove dissolved salts, bacteria, and various contaminants. | Thin-film composite (TFC) or cellulose acetate membranes |
| 4. Post-treatment | Adjusts water chemistry for stability and safety, including deionization or disinfection as needed. | Electrodeionization (EDI), UV sterilizers, chemical dosing units |
This multi-stage process ensures that water meets stringent purity expectations while optimizing membrane lifespan and system efficiency.
4. Key Components of Commercial RO Systems Explained
4.1 Multimedia Filters
These filters remove large particulates and suspended solids from raw water using layers of sand, anthracite, and gravel. Their robust design prevents clogging downstream, reducing membrane fouling.
4.2 Activated Carbon Filters
They effectively adsorb chlorine and organic compounds that could degrade membranes and cause undesirable taste or odor in treated water.
4.3 Water Softeners
Softening removes hardness ions like calcium and magnesium, preventing scale formation on membranes which is a major cause of performance decline and maintenance costs.
4.4 High-Pressure Pumps
These pumps supply the hydraulic pressure essential for forcing water through membranes. Their specifications must match feed water characteristics and desired system throughput.
4.5 Reverse Osmosis Membranes
The heart of the system, membranes are specialized films that selectively permit water molecules while rejecting contaminants. The most common types include thin-film composite (TFC) membranes known for high rejection rates and durability.
5. Membrane Technology and Maintenance Recommendations
Choosing the right membrane type and maintaining it judiciously is pivotal for system longevity and operational cost-effectiveness. TFC membranes offer high resistance to bacteria and chemical agents, suitable for most commercial uses.
- Cleaning Protocols: Periodic chemical cleaning using acid and alkaline solutions removes fouling agents such as scale and biofilm, restoring permeability.
- Replacement Cycle: Membranes typically last 3-5 years depending on feed water quality and maintenance rigor.
- Monitoring: Implementing online monitoring for pressure differentials and permeate quality helps predict membrane replacement timing efficiently.
Proper maintenance not only extends membrane life but reduces downtime and improves overall water production stability.
6. Post-treatment Techniques for Water Quality Enhancement
After RO filtration, additional treatment steps ensure water meets specific use-case requirements:
- Mixed Bed Deionization (MBDI): Further removes ionic contaminants to produce ultra-pure water.
- Electrodeionization (EDI): A continuous process that complements RO by electrically removing ions without chemical additives.
- Ultraviolet (UV) Sterilization: Destroys microbial contaminants, providing a final barrier against bacteria and viruses.
- Re-Mineralization: In some cases, post-treatment adds desirable minerals back for taste or application-specific water quality (especially in beverage industry).
These steps are vital to ensure water safety and compliance with regulatory standards.
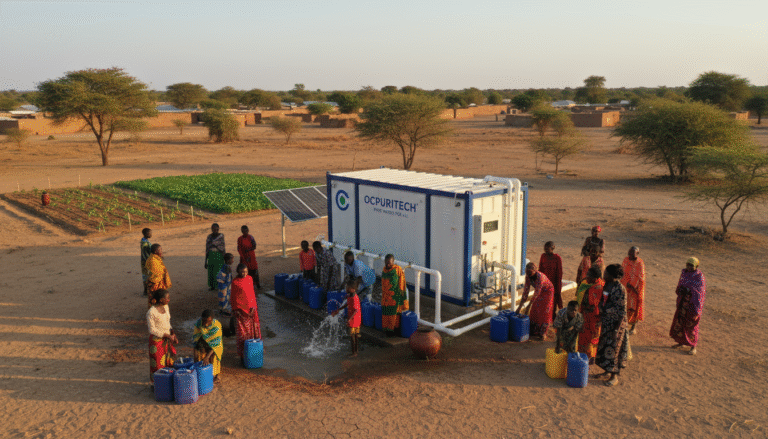
7. Exemplary Industry Applications of Commercial RO Systems
The versatility of commercial reverse osmosis water purification systems is evident across multiple sectors:
7.1 Food and Beverage Processing
RO systems guarantee the purity necessary for ingredient consistency and product safety. For instance, in a beverage bottling plant I advised, implementing a whole house RO system improved taste profiles and reduced microbial counts by 99.9%, increasing shelf stability.
7.2 Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Pharma-grade water demands ultra-pure standards. An industrial RO system integrated with EDI and UV ensured compliance with USP water for injection requirements at a regional drug manufacturer, reducing batch contamination risks.
7.3 Textile Industry
High-quality water reduces fabric defects and chemical usage. A textile mill I supported used a commercial RO water system, leading to 30% lower chemical consumption and improved dye penetration uniformity.
7.4 Hospitality Sector
Hotels utilize RO treated water for guest services and kitchen operations to improve taste, odor, and equipment lifespan, enhancing customer satisfaction and lowering maintenance.
8. Pricing Factors Influencing Commercial RO Systems
The investment cost of commercial RO equipment varies based on the following major factors:
| Factor | Impact on Pricing |
|---|---|
| Material and Component Quality | Higher-grade membranes, pumps, and housings increase upfront costs but improve durability |
| Customization Level | Tailored systems for specific feed water conditions or output demands require engineering and integration effort |
| Capacity and Throughput | Larger systems naturally entail higher capital investments |
| Operational Cost Projections | Energy-efficient designs may have higher initial cost but lower lifecycle expenses |
| After-Sales Support and Warranty | Comprehensive service agreements add value but affect total ownership cost |
Businesses should weigh these factors alongside financing options to achieve an optimal return on investment.
9. Installation and After-Sales Support: Ensuring Long-Term Success
Professional installation is paramount to ensure system performance. Preparations include site evaluation, feed water testing, and infrastructure readiness such as plumbing and electrical connections.
Installation phases typically progress through equipment setup, commissioning, performance validation, and user training. In my experience assisting multiple industrial clients, onsite training significantly reduces operator errors and enhances system reliability.
Long-term support encompasses scheduled maintenance, remote monitoring, spare parts provisioning, and technical hotline services, collectively maximizing uptime and user confidence.
10. Maintenance and Troubleshooting Guidelines
Regular maintenance strategies are crucial for preventing performance degradation:
- Routine Filter Changes: Replacing pre-filters avoids membrane damage by protecting against particulates.
- Monitoring Pressure and Flow: Sudden changes often indicate fouling or mechanical issues.
- CIP (Clean-In-Place) Procedures: Safe chemical cleaning protocols tailored to specific fouling types extend membrane lifespan.
Common troubleshooting steps include identifying causes of low permeate flow, elevated differential pressure, or poor rejection rates. Access to quality replacement parts is essential for quick rectification.
11. Manufacturers and Market Positioning
Leading manufacturers of commercial RO water treatment systems distinguish themselves through advanced R&D, adherence to international quality standards (e.g., NSF, ISO certifications), and responsive global service networks.
The competitive landscape reflects innovation in membrane technology, energy recovery devices, and process automation, aligning with evolving customer demands and regulatory frameworks worldwide.
12. Conclusion: Embracing Reverse Osmosis for Superior Water Quality
Selecting the right reverse osmosis water system is a strategic decision that profoundly impacts operational efficiency, product quality, and compliance. As demonstrated, commercial RO equipment delivers unmatched purity through sophisticated multi-stage processes backed by reliable components and maintenance regimes.
Incorporating comprehensive pre-treatment, advanced membranes, and post-treatment technologies secures water quality tailored for diverse industrial needs. Supported by authoritative market data and enriched by practical case studies, this guide illuminates the path toward adopting and optimizing commercial reverse osmosis systems for sustainable success.
For stakeholders seeking enhanced water treatment solutions, engaging with expert providers for system design, integration, and after-sales service ensures maximal benefits and operational continuity.
References
- Grand View Research – Water Treatment Systems Market Size, Share Report 2030
- Archive Market Research – Commercial and Industrial RO Water Treatment Equipment Decade Long Trends, Analysis and Forecast 2025-2033