Overview of Ultrafiltration Drinking Water Systems
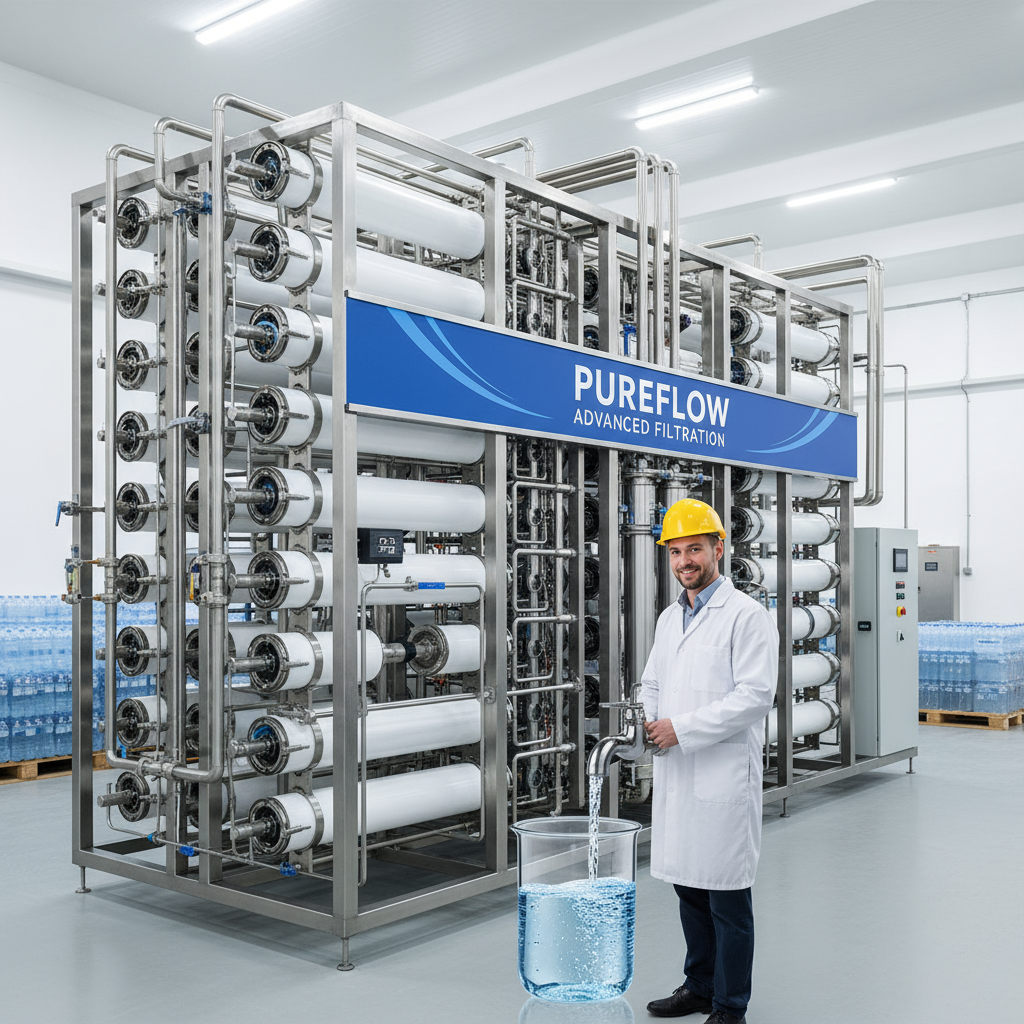
The ultrafiltration drinking water system represents a cutting-edge technology widely used for water purification across various industries. These systems employ semi-permeable membranes to remove suspended solids, bacteria, viruses, and colloidal particles from water, ensuring clean and safe drinking water. Their applications span municipal water treatment, industrial processing, and even residential use.
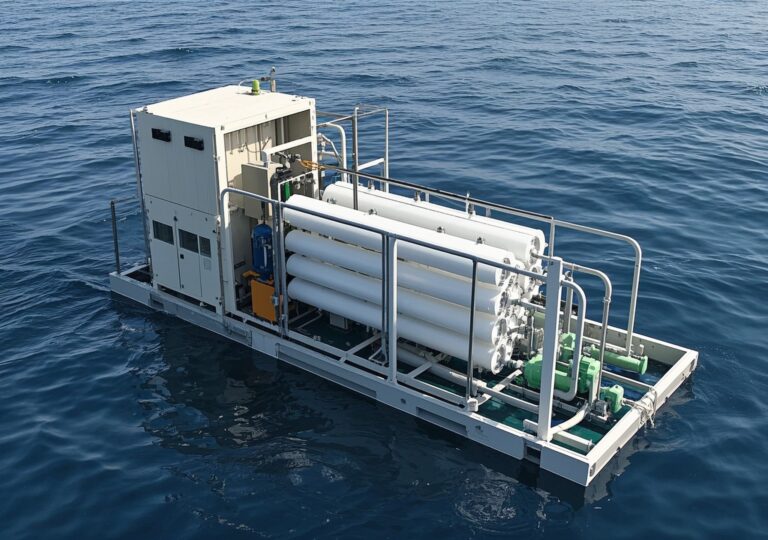
Industries benefiting from ultrafiltration include mining, food and beverage production, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics manufacturing, and laboratory environments. Additionally, ultrafiltration is instrumental in treating diverse water sources such as groundwater, river water, municipal tap water, well water, boiler feed water, and ultrapure water preparation.
The robust capability of ultrafiltration systems to handle varied feed waters with fluctuating turbidity and microbial loads makes them indispensable in increasingly stringent water quality scenarios.
Technical Principles and Key Components
At the heart of the ultrafiltration drinking water system lies membrane technology characterized by pore sizes ranging approximately from 0.01 to 0.1 microns. This allows effective separation of particles larger than the membrane pores while permitting water and low molecular weight solutes to pass.
The filtration operates under pressure-driven mechanical separation without requiring chemicals, thus preserving the water’s chemical composition. Key components include:
- Ultrafiltration Membranes: Typically made from polymeric materials such as polyethersulfone (PES) or polysulfone (PS), and increasingly ceramic membranes for enhanced chemical and thermal stability.
- Membrane Housing: Pressure vessels designed to contain membrane modules and withstand operational pressures.
- Pumps and Piping: For feed water pressurization and flow management.
- Automatic Control Systems: Incorporate sensors and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to optimize operation, monitor membrane fouling, and automate cleaning cycles.
- Cleaning Systems: Employing backwashing and chemical cleaning to maintain membrane performance over long operational periods.
Advanced ultrafiltration systems feature modular designs enabling scalability and ease of maintenance. The reduction in energy consumption compared with traditional filtration methods further positions ultrafiltration as a sustainable choice.
Price Structure and Return on Investment
Investment in an ultrafiltration drinking water system encompasses several cost components:
| Cost Component | Description | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| Base System | Includes membrane modules, housings, pumps, and control units. | 40%–60% of total CAPEX |
| Installation and Integration | Site preparation, piping, instrumentation, and electrical integration. | 15%–25% |
| Additional Modules | Pre-treatment equipment (e.g., sediment filters) and post-treatment (e.g., UV sterilizers). | 10%–20% |
| Operation and Maintenance | Membrane cleaning chemicals, labor, energy consumption. | Ongoing operational cost, typically 5%–10% annually |
The total cost-effectiveness derives from lower energy usage, chemical-free operation, and long membrane lifespans. In industrial settings, ultrafiltration reduces downtime and wastewater discharge penalties, contributing to operational savings.
Performance Specifications and Quality Assurance
Typical ultrafiltration systems achieve the following performance metrics:
- Removal Efficiency: >99.9% bacteria and viruses, turbidity reduction to below 0.1 NTU
- Flow Capacity: Modular scalability from hundreds to thousands of liters per hour, tailored to applications
- Operating Pressure: Typically 1 to 5 bar
- Membrane Lifetime: 3 to 7 years depending on feed water quality and maintenance
- Material Compliance: Certified food-grade materials and compliance with NSF/ANSI standards
Quality assurance includes strict membrane integrity testing, hydraulic performance checks, and process control validation to maintain reliable water quality.
Market and Application Context
The rising global demand for safe and clean drinking water drives strong growth in ultrafiltration systems’ adoption. According to Grand View Research, the ultrafiltration market size reached approximately $3.08 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a 7.4% CAGR through 2030, reflecting sustained investments in municipal and industrial water treatment infrastructure.
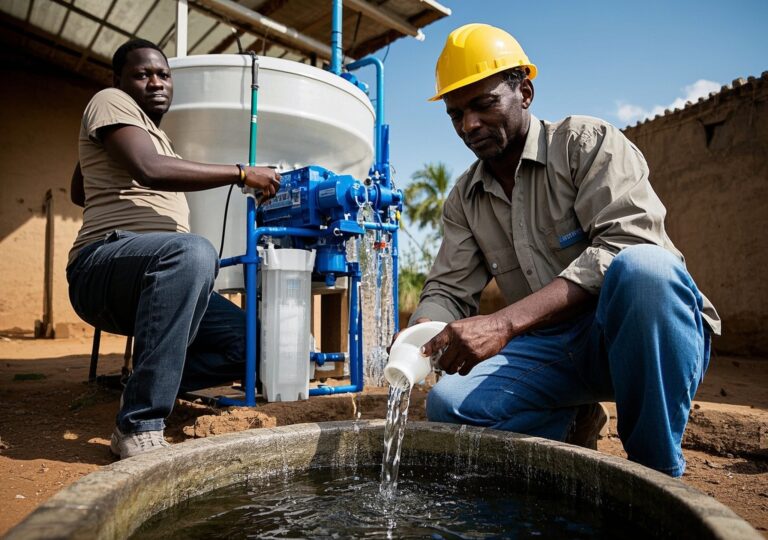
Regions with limited water resources or high pollution levels particularly benefit from ultrafiltration. For instance, industrial zones with stringent discharge regulations leverage these systems to recycle process water and minimize environmental impact. The technology’s chemical-free operation aligns with growing ecological sustainability mandates.
Case Studies: Practical Applications and Outcomes
Drawing from direct experience, I highlight three distinct scenarios demonstrating the ultrafiltration drinking water system’s effectiveness:
- Pharmaceutical Facility in Europe: In a pharmaceutical manufacturing plant, we integrated an ultrafiltration system to treat boiler feed water. The system consistently achieved bacterial rejection rates above 99.99% and reduced particulate load, leading to a 30% reduction in boiler maintenance costs over 24 months. Automation allowed seamless operation with minimal labor, aligning with GMP compliance standards.
- Municipal Water Plant in Asia: Retrofit of an existing treatment plant with ultrafiltration modules resulted in turbidity reduction from >5 NTU to <0.1 NTU, eliminating the need for chlorination downstream. This improved water taste, odor, and overall community satisfaction. The plant saw a 25% reduction in chemical costs and accelerated throughput capacity.
- Food Processing Facility in North America: The system was customized to treat both process water and wastewater streams. Delivering reliable removal of oil emulsions and suspended solids, it enabled water reuse and lowered fresh water intake by 40%, contributing to sustainability certification and operational savings.
Customized Solutions and Comprehensive Service Support
Customization is integral to ultrafiltration system deployment. Depending on feed water characteristics, pre-treatment options such as sediment filtration, pH adjustment, or anti-scalant dosing can be incorporated. Post-treatment modules including UV disinfection or activated carbon filters further enhance water quality.
Installation services encompass site assessment, system integration with existing infrastructure, and staff training. Ongoing support includes scheduled maintenance, membrane cleaning, performance monitoring, and rapid technical response to ensure minimal downtime.
Manufacturers’ Technological Strength and Strategic Cooperation
Leading manufacturers excel by combining membrane innovation, automation technology, and quality management systems. Certifications such as ISO 9001 and NSF/ANSI attest to product reliability. Collaborative projects with research institutions facilitate continuous product improvement tailored to evolving water quality challenges.
Partnerships between manufacturers, consulting engineers, and end users foster value-driven solutions that maximize system lifespans and operational efficiency, strengthening water security for communities and enterprises.
Conclusive Insights and Investment Considerations
In summary, the ultrafiltration drinking water system offers a compelling solution for high-quality water treatment due to its microbial rejection, chemical-free operation, and adaptable application range. The growing market data and successful operational case studies reinforce its commercial viability.
For prospective investors and water treatment managers, optimizing ultrafiltration system deployment involves:
- Selecting membrane materials and module configurations suited to feed water profiles
- Implementing integrated pre- and post-treatment to safeguard membrane longevity
- Adopting automation for enhanced operational control and reduced labor costs
- Leveraging regional incentives for water reuse and environmental compliance
These strategies ensure balanced capital expenditure with operational savings, delivering sustainable water quality improvements aligned with future regulatory trends.
Ultimately, embracing ultrafiltration technology embodies the bold experience and confidence to rely on clean, efficient water purification for diverse industrial and municipal needs.
References
- Grand View Research – Ultrafiltration Market Size & Share | Industry Report, 2030
- Fact.MR – Ultrafiltration Market Size, Demand & Growth Report by 2033
- Data Bridge Market Research – Global Ultrafiltration Market Size, Share, and Trends Analysis Report – Industry Overview and Forecast to 2032
- MarketsandMarkets – Ultrafiltration Market Size ($4.07 billion) 2030