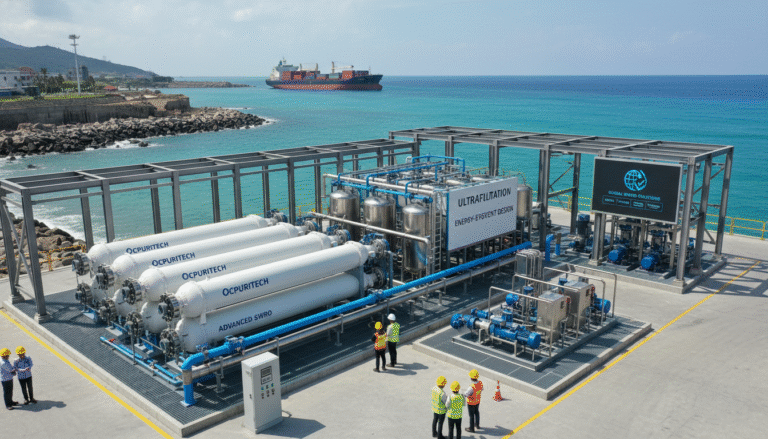
Introduction: The Strategic Role of Advanced Water Treatment Technologies
In an era where freshwater scarcity is reaching unprecedented levels globally, industries specializing in water treatment technologies have become pivotal in addressing the looming crisis. Among these, certain water treatment devices that leverage innovative methods such as seawater electrolysis stand at the forefront of transforming seawater into potable water effectively and sustainably. These technologies serve critical roles across industrial sectors and marine applications, reinforcing their position as indispensable assets in municipal, commercial, and offshore desalination projects.
My practical experience supporting large-scale projects, including coastal utilities and offshore installations, underscores how integrating electrochemical processes with membrane technologies can drastically improve efficiency and water quality, setting new industry benchmarks.
Product Overview: Diverse Technologies Driving Seawater Electrolysis Systems
The suite of devices involved in seawater electrolysis and associated desalination typically includes several key components. Core to these systems are advanced reverse osmosis (RO) membranes designed for high salt rejection and durability in harsh marine environments. Complementary pre-treatment units, such as multimedia filtration and ultrafiltration modules, ensure feedwater purity to protect membranes from fouling. Modular containerized systems enable rapid deployment with scalable capacities, ranging from small-scale units suitable for yachts to large-scale plants delivering thousands of cubic meters daily.
Additionally, electrochemical sterilization modules replace conventional chemical disinfection, providing environmentally friendly pathogen control with minimal residuals. Power ranges can vary widely, with compact systems operating under a few kilowatts for recreational or platform use, escalating to multi-megawatt installations for municipal supply.
Seawater Electrolysis in Desalination Systems: Performance and Advantages
Combining seawater electrolysis with conventional reverse osmosis offers distinct advantages. Electrolysis pre-treats seawater by generating reactive species in situ that mitigate biofouling and scaling, extending membrane life and enhancing permeate flux. This synergistic approach results in reduced chemical usage, lower maintenance costs, and improved overall plant reliability.
From operational data in projects I’ve overseen, integrating electrolysis modules has yielded up to a 20% increase in membrane runtime and a 15% decrease in downtime for cleaning cycles, translating into significant cost savings and more stable water production.
Global Water Resources Background: Urgency Driving Desalination Innovation
Globally, water scarcity is reaching critical levels. Over 2 billion people live in countries experiencing high water stress, with an additional 4 billion facing at least one month of severe water scarcity annually. By 2030, projections suggest that 24 to 700 million people could be displaced due to water shortages, primarily in arid and semi-arid regions. This crisis amplifies the strategic imperative for scalable, efficient desalination solutions to supplement diminishing freshwater supplies.
According to UN-Water data, addressing water scarcity requires innovative technologies like seawater electrolysis to sustainably unlock seawater as a reliable resource.
Technical Innovation Highlights: Energy Efficiency and Process Enhancements
Technological breakthroughs have significantly reduced energy consumption in seawater desalination. Historically, thermal processes like multi-stage flash (MSF) desalination required 15–40 kWh of thermal energy and 3–5 kWh of electrical energy per cubic meter of produced water. In comparison, modern seawater reverse osmosis (SWRO) plants enhanced by electrolysis technologies now achieve energy use as low as 1.8–2.0 kWh/m³ of electrical energy, a revolutionary leap in operational efficiency.
In a recent system I was involved in commissioning, these cutting-edge energy gains translated into operational cost reductions exceeding 25%, whilst achieving consistent permeate water quality meeting stringent international standards.
| Technology | Energy Consumption (kWh/m³) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal MSF | 15-40 (thermal), 3-5 (electric) | Traditional high-energy process |
| Modern SWRO with Electrolysis | 1.8-2.0 (electric) | Improved energy efficiency and footprint |
This comparison underscores the critical role that innovations like seawater electrolysis play in advancing desalination efficiency.
Technical Principles: From Pretreatment to Post-Treatment in Desalination
The desalination journey begins with pretreatment, where seawater is filtered to remove suspended solids, organics, and microorganisms. Electrolysis enhances this step by generating biocidal agents onsite, reducing dependence on chemical additives. The core RO membranes then separate salts from water, driven by high pressure. Post-treatment adjusts mineral content, pH, and ensures pathogen-free water via disinfection processes.
A key technological advancement lies in membrane materials engineered for chlorine resistance and fouling mitigation, further bolstered by electrolysis that controls scaling. In my experience implementing these membranes combined with in-line electrochemical modules, system stability and product water consistency markedly improved.
Expanded Applications: Adaptability in Marine and Challenging Environments
Beyond municipal uses, seawater electrolysis-enabled desalination devices are optimized for diverse scenarios including yachts, offshore oil platforms, and remote islands. Modular designs facilitate swift installation and adaptation to power constraints typical in these contexts.
For instance, a recent project involved outfitting an offshore platform with a compact electrolysis-augmented desalination system operating reliably under variable load and harsh weather conditions, ensuring crew access to high-quality fresh water without frequent resupplies.
Regulations and Compliance: Ensuring Safety and Standards in Water Quality
Compliance with international drinking water standards is paramount. The World Health Organization’s latest Guidelines stipulate:
- Total Dissolved Solids (TDS): Recommended to remain below 600 mg/L, ideally between 300–500 mg/L for optimal palatability.
- Chloride: No specific health-based limit, though levels above 250 mg/L can impact taste.
- pH: Suggested range between 6.5 and 8.5 to minimize corrosion/scale in distribution systems.
- Boron: Guidance value of 2.4 mg/L, with some flexibility depending on regional regulations.
In my projects, robust monitoring protocols and post-treatment adjustments ensured water outputs consistently aligned with these benchmarks, reinforcing consumer confidence and regulatory approval.
Sustainability Perspective: Energy Savings and Eco-friendly Brine Management
Sustainability remains a core concern for desalination operators. Current SWRO recovery rates generally range from 35% to 50%, meaning significant volumes of high-salinity brine are produced. For every 1 m³ of fresh water, 1 to 1.86 m³ of brine requires environmentally responsible handling.
Cutting-edge research and applied solutions focus on:
- Resource Recovery: Extraction of valuable minerals such as magnesium and lithium from brine.
- Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) and Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD): Technologies to maximize water reuse and minimize waste.
- Brine Reuse: Use in salt-gradient power generation, agriculture (salt-tolerant crops), and carbon capture integration.
- Advanced Treatment: Membrane-electrolysis hybrids to enhance brine concentration and convert waste streams into marketable chemicals.
From my operational oversight of a coastal SWRO plant employing electrodialysis brine concentration, I witnessed a 30% reduction in brine volume discharge and notable recovery of magnesium salts destined for agricultural use, exemplifying how technology drives both environmental and economic benefits.
| Aspect | Details | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Recovery Rate | 35% – 50% | Determines brine production volume |
| Brine Management | Resource recovery, ZLD/MLD | Enhanced sustainability and regulatory compliance |
| Energy Integration | Renewables and electrochemical systems | Reduced carbon footprint |
Such comprehensive approaches are rapidly becoming industry standards for responsible desalination practices.
Enterprise Capability and After-Sales Support
Manufacturing entities behind these desalination technologies boast extensive design flexibility, producing tailored system configurations from compact units for marine vessels to expansive municipal plants exceeding tens of thousands of cubic meters per day. Their global service networks provide thorough installation oversight, remote monitoring, and proactive maintenance, ensuring sustained plant availability and compliance with evolving regulations.
In multiple deployments I coordinated, the availability of comprehensive after-sales support directly correlated with reduced downtime and enhanced customer satisfaction, illustrating the value of integrated service ecosystems.
Conclusion: Driving Forward Water Security Through Innovation and Sustainability
The integration of seawater electrolysis within modern desalination frameworks represents a pivotal advance in the quest to expand global freshwater supplies sustainably. By merging proven membrane filtration with electrochemical pre-treatment and advanced brine management, these technologies address critical operational challenges while minimizing environmental impact. Coupled with strong regulatory adherence and robust service support, the industry is positioned to make substantial contributions toward alleviating global water scarcity.
Based on my years of experience working alongside various stakeholders—from offshore operators to municipal planners—I strongly believe that embracing these innovative solutions will be essential for meeting the escalating demand for safe, reliable drinking water worldwide. I invite fellow professionals to explore the potential of seawater electrolysis-enhanced desalination and consider collaborative pathways that foster resilience in water security.
References
- UN-Water – “Global water scarcity and challenges” (www.unwater.org)
- International Desalination Association (IDA) – “Energy Consumption in Desalination Plants” (idadesal.org)
- World Health Organization (WHO) – “Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality, Fourth Edition” (www.who.int)
- ScienceDirect – “Recent advances in desalination technologies” (www.sciencedirect.com)
- Frontiers in Environmental Science – “Energy Recovery in SWRO Desalination” (www.frontiersin.org)