Zing of Progress: How Water Treatment Careers Propel RO Systems
Water is the lifeblood of modern industry, and its purity and availability underpin everything from food safety to pharmaceutical manufacturing. Among various purification methods, commercial reverse osmosis (RO) systems stand out for their efficiency and reliability in providing high-quality water. This article delves into the fundamentals, technology, and industry applications of commercial RO systems while also highlighting the expanding water treatment careers that drive this sector’s progress. Drawing from authoritative data and real-world experience, we illuminate how careers in this field empower both innovation and operational excellence.
1. Introduction: The Essence of Commercial Reverse Osmosis Water Treatment
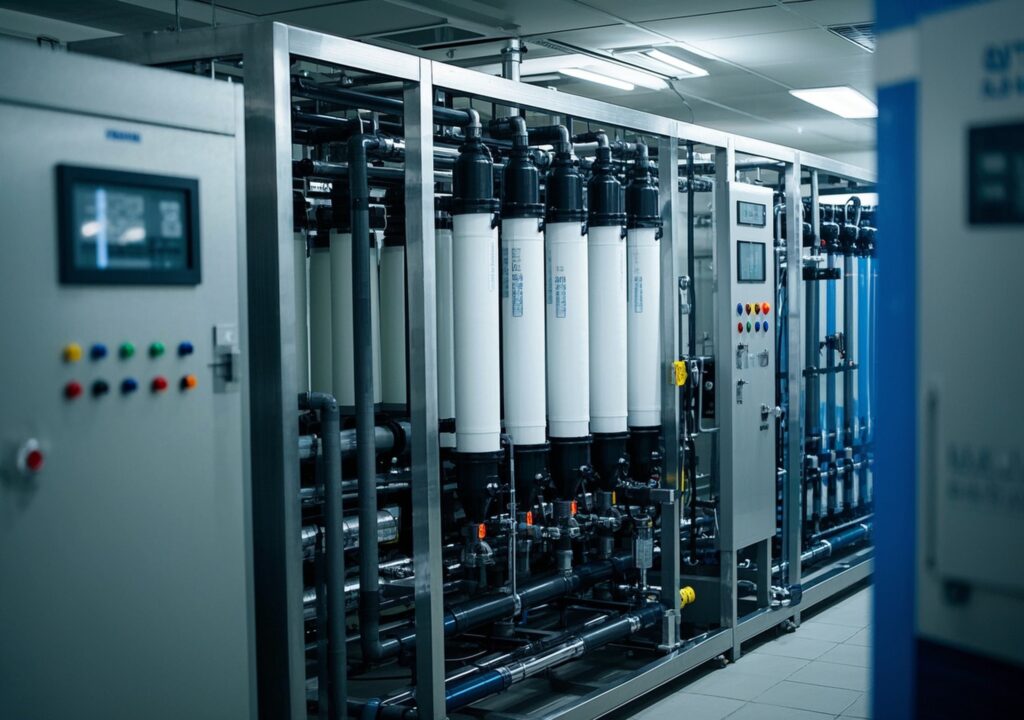
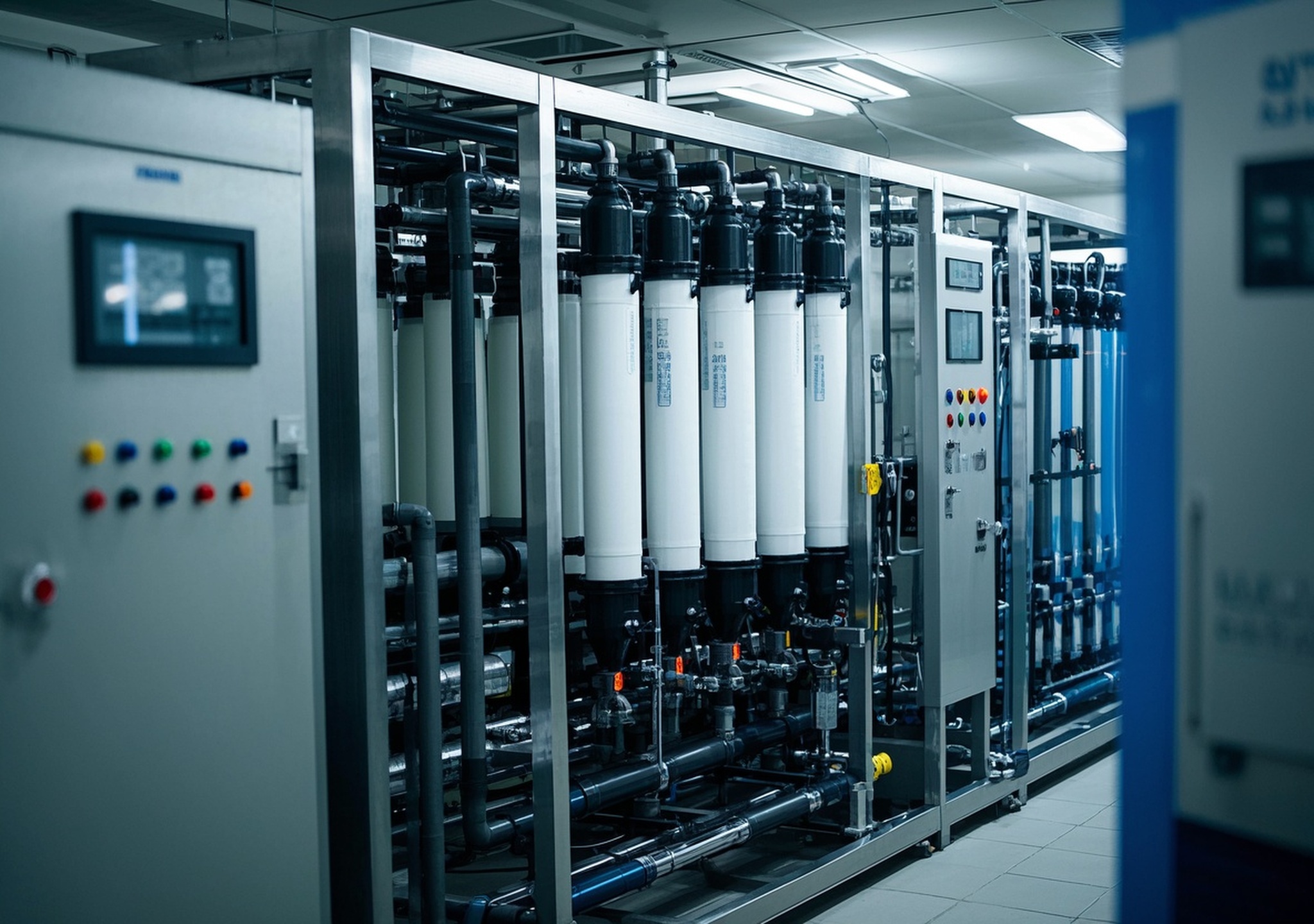
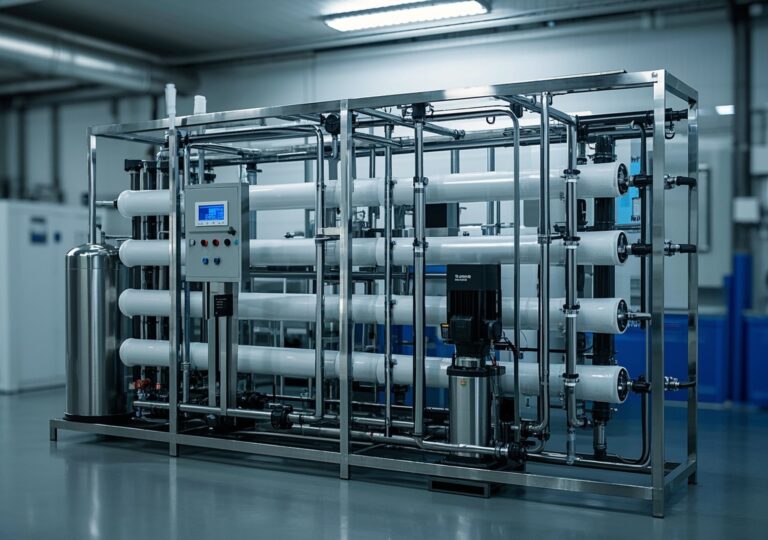
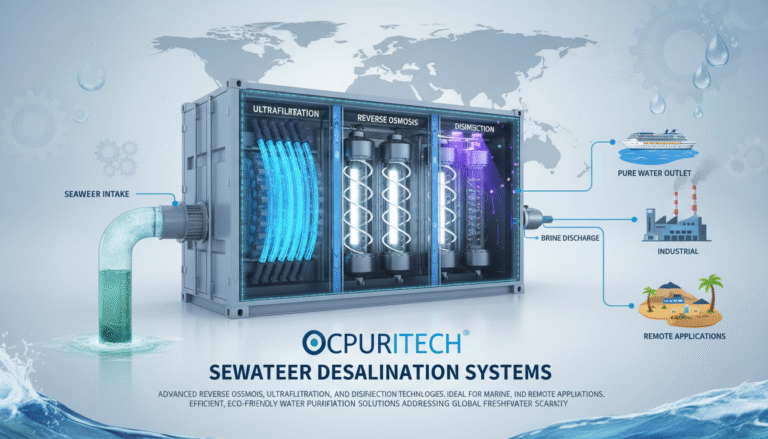
Commercial reverse osmosis systems use a semi-permeable membrane to remove dissolved salts, bacteria, and other contaminants from water. These systems are extensively applied across industries requiring ultra-pure water such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, textiles, and hospitality. The urgency to enhance water quality stems not only from regulatory demands but also from increasing sustainability goals within industrial operations.
In my consulting experience with municipal water utilities and industrial plants, I’ve witnessed RO systems go from niche solutions to core components in water management strategies. This shift reflects growing technical sophistication and the rising demand for skilled practitioners.
2. Equipment Overview and Performance Advantages
Commercial RO systems typically process anywhere from thousands to millions of gallons per day, depending on industrial scale. They feature robust construction designed to withstand varying feed water qualities and pressures.
| Performance Parameter | Typical Range | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Feed Water Flow Rate | 10,000 – 1,000,000+ GPD | Adapts to diverse industrial demands |
| Salt Rejection Rate | ≥ 98% | Ensures water meets purity criteria |
| Operating Pressure | 150 – 600 psi | Optimizes membrane performance |
| Recovery Rate | 75% – 85% | Maximizes water recovery, lowers waste |
The core advantage of modern RO systems lies in their modular design and computer-controlled operations, allowing continuous monitoring and optimization to reduce energy consumption and downtime.
3. Process Flow: From Raw Water to Purified Output
Understanding the workflow in a commercial RO system is imperative for professionals within water treatment careers. The process unfolds in these distinct stages:
- Pre-treatment: Raw water undergoes filtration through multimedia and activated carbon filters to remove particulates, chlorine, and organics that could damage membranes.
- Softening: In many systems, water softeners reduce hardness ions (calcium and magnesium) to prevent scaling on membranes.
- High-Pressure Pumping: Specialized pumps increase water pressure to force feed water through membranes.
- Reverse Osmosis Membrane Filtration: Semi-permeable membranes separate dissolved solids from purified water.
- Post-treatment: Additional polishing steps, including pH adjustment, UV sterilization, or ion exchange, enhance water quality to meet specific application needs.
The accompanying process flow diagram below illustrates these steps clearly:
[Process Flow Diagram: Pre-treatment → Softening → High-pressure pump → RO membranes → Post-treatment]
4. Key Components Detailed
Each major component within a commercial RO system fulfills a critical function:
| Component | Function | Technical Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Multimedia Filter | Removes suspended solids and turbidity | Layered media with gravel, sand, and anthracite; backwashable |
| Activated Carbon Filter | Adsorbs chlorine and organic compounds | Granular or block carbon with high adsorption capacity |
| Water Softener | Removes hardness ions to protect membranes | Ion exchange resins, regenerable with salt brine |
| High-Pressure Pump | Pressurizes feed water to membrane | Energy-efficient centrifugal or positive displacement pumps |
| RO Membrane Modules | Separates impurities from water | Thin film composite membranes with high salt rejection |
In a recent deployment I managed at a textile manufacturing plant, selecting high-efficiency pumps reduced operational energy costs by 12%, significantly enhancing ROI.
5. Membrane Technology and Maintenance Tips
RO membranes vary from cellulose acetate to thin-film composite types. The latter dominate commercial applications due to superior salt rejection and chlorine resistance.
Key membrane performance indicators include:
- Salt Rejection Rate (typically ≥98%)
- Flux Rate (GFD – gallons per square foot per day)
- Operating Pressure and pH Range
Proper maintenance is crucial to maximize lifespan (typically 3-5 years):
- Regular chemical cleaning protocols to prevent fouling
- Monitoring feed water quality to avoid scaling
- Using anti-scalants and biocides as preventive aids
- Timely replacement of membranes showing performance drops
From my experience overseeing municipal water treatment upgrades, compliance with preventive maintenance schedules has extended membrane life by up to 40%, yielding cost savings and operational stability.
6. Advanced Post-treatment Techniques
Ensuring water meets stringent purity criteria often requires complementary technologies after RO filtration:
- Mixed Bed Deionization (MBDI): Polishing water to ultra-pure standards by removing residual ions.
- Electrodeionization (EDI): A continuous process replacing traditional chemical regeneration methods, reducing chemical waste.
- Ultraviolet (UV) Disinfection: Eliminates microbiological contaminants without chemicals.
In pharmaceutical settings I’ve consulted for, combining RO with UV disinfection ensures compliance with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) requirements and prevents costly contamination events.
7. Application Case Studies Across Industries
Food and Beverage
Commercial RO provides purified water for beverages, removing undesirable taste and contaminants. In a soft drink manufacturing site, the installed RO system lowered total dissolved solids (TDS) to under 50 ppm, improving flavor consistency and product shelf life.
Pharmaceutical Industry
Water for injection (WFI) and other pharmaceutical waters demand ultra-high purity standards. Integrating RO with MBDI and UV post-treatment achieves endotoxin-free water meeting pharmacopeia standards. My team supported a biotech firm’s upgrade, resulting in a 30% reduction in water waste and optimized batch production.
Textile Manufacturing
RO systems remove hardness and dissolved salts that affect dyeing quality and fabric integrity. At a large-scale textile plant, implementation of RO units led to 25% savings in chemical usage for rinsing and washing processes.
Hospitality Sector
Hotels rely on pure water for guest services, kitchen use, and boilers. RO systems ensure water taste and safety, enhancing guest satisfaction and reducing maintenance downtime.
8. Pricing Influences and Investment Considerations
The cost of commercial RO systems depends on several factors including:
| Factor | Impact on Pricing | Investor Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Component Quality | Higher quality raises upfront cost but reduces downtime | Long-term savings and reliability |
| Customization | Tailored solutions cost more than standard units | Greater process fit and efficiency gains |
| Operating Expenses | Energy, maintenance, and replacement parts | Evaluate total cost of ownership, not just purchase price |
| Financing Options | Leasing and service contracts can offset capital expenditure | Improves cash flow management |
In a project I advised involving a beverage company, shifting to high-efficiency membranes and optimized pump systems led to a break-even point within 2.5 years due to reduced energy and chemical costs.
9. Installation and After-sales Support
Successful system deployment depends on thorough site assessment and preparation. Typical installation steps include:
- Pre-installation survey and feed water analysis
- Foundation and piping setup
- Mechanical and electrical installation
- System commissioning and performance testing
- Operator training on system use and maintenance
Long-term technical support covering troubleshooting, spare parts provisioning, and software updates is crucial. From direct involvement in multiple installations, I can attest that meticulous operator training yields fewer operational errors and enhances system longevity.
10. Maintenance Guidelines and Troubleshooting
Routine maintenance keeps RO systems running efficiently and includes:
- Frequent pre-filter and cartridge changes
- Monitoring pressure differentials to detect fouling
- CIP (clean-in-place) chemical cleaning schedules
- Membrane integrity testing
Common faults include membrane scaling, pump cavitation, and electronics malfunctions. Having ready access to certified spare parts and technical service prevents prolonged downtime.
11. Manufacturers and Market Positioning
Leading commercial RO system manufacturers offer products certified to standards such as NSF/ANSI, ISO 9001, and UL. They typically maintain global manufacturing footprints to ensure fast delivery and support.
Based on market trends and end-user feedback, companies emphasizing modular designs, IoT-enabled remote monitoring, and energy efficiency are gaining competitive advantage. This reflects a broader industry pivot towards intelligent water treatment.
12. Conclusion and Call to Action
Choosing the right commercial RO system can profoundly impact operational sustainability, regulatory compliance, and product quality. The depth of expertise within water treatment careers fuels continuous advancement in membrane technology, process optimization, and system integration.
For industries seeking to enhance water purity while balancing costs and environmental impact, investing in well-designed RO solutions and skilled workforce development is imperative. If you aim to future-proof your water treatment infrastructure, consider partnering with experienced professionals who understand both the technology and real-world operational demands.
The evolving landscape of water treatment presents robust career opportunities, from system design to operation and maintenance. Embracing these challenges not only advances water technology but also safeguards a vital resource for generations to come.
References
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics – Occupational Outlook Handbook, Water and Wastewater Treatment Plant and System Operators, May 2024
- Data USA – Water & Wastewater Treatment Plant & System Operators, 2023 data
- Grand View Research – Water And Wastewater Treatment Equipment Market Report, Projection through 2030