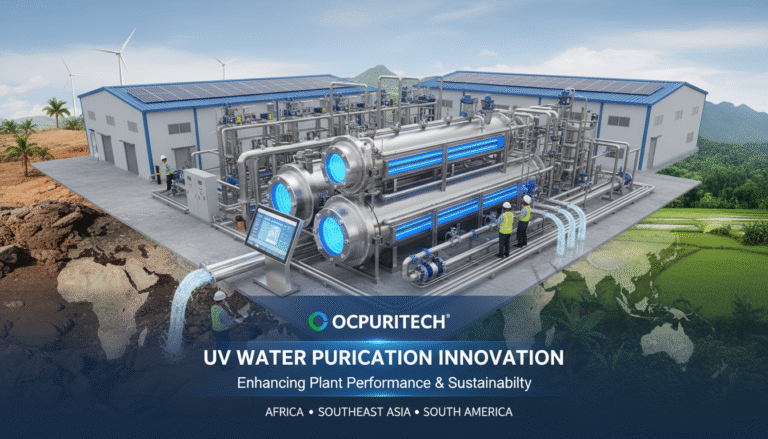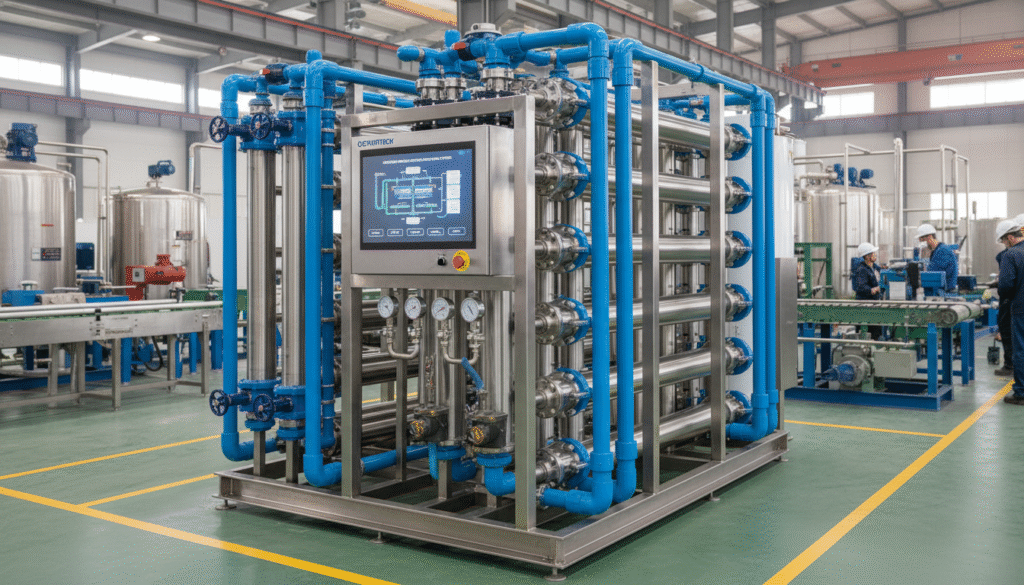
Industrial water treatment has become indispensable for a vast range of sectors aiming to optimize operational efficiency and comply with stringent environmental regulations. Among these technologies, the industrial ultrafiltration system stands out as a precise and reliable solution for removing suspended solids, bacteria, and colloidal particles from diverse water sources. This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of industrial ultrafiltration systems, including their core technologies, pricing components, performance standards, and practical applications. Drawing from both authoritative data and my own extensive project experience, I’ll share insights to help you boost your plant’s efficiency and sustainability.
Product Overview: Types, Functions, and Industries Served

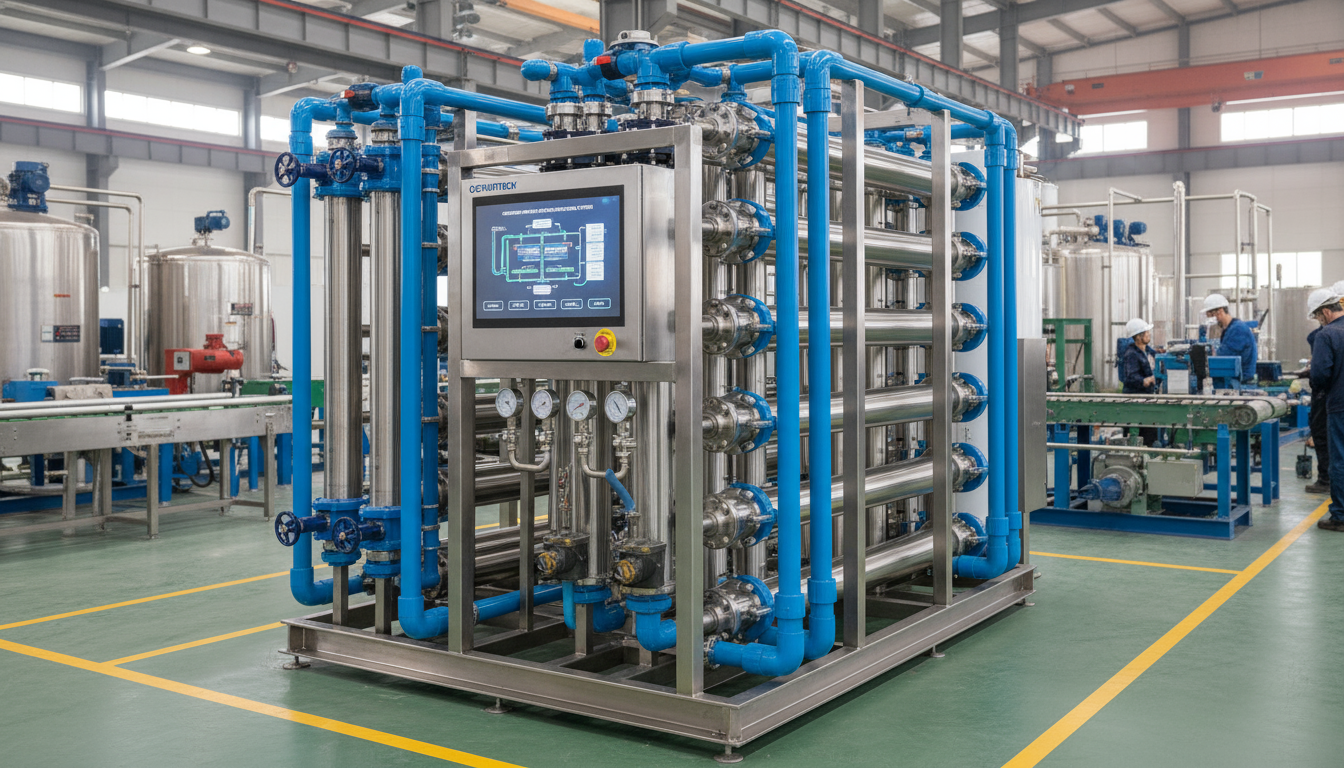
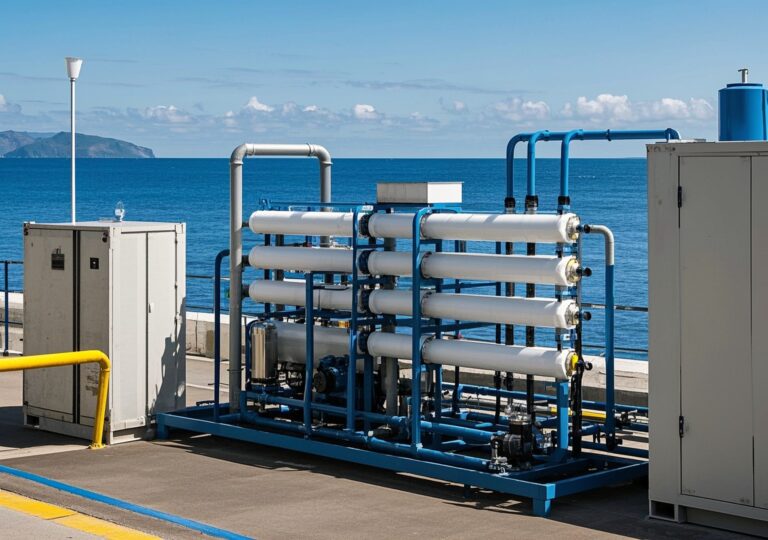
At its core, an industrial ultrafiltration system is a membrane-based filtration technology designed to separate microscopic impurities—such as suspended solids, pathogens, and high-molecular-weight solutes—from water. These systems are highly versatile and applicable across industries including mining, food processing, cosmetics manufacturing, pharmaceutical production, laboratories, and municipal water treatment. They are also tailored for various feed water types like river water, groundwater, well water, boiler feedwater, and ultrapure water for sensitive applications.
Ultrafiltration membranes offer pore sizes typically ranging from 0.01 to 0.1 microns, effectively filtering out contaminants without the need for chemical additives. Their modular design allows integration with pretreatment units such as sand filters and carbon filters, as well as post-treatment processes where necessary.
In my experience working on a beverage production facility installation, the ultrafiltration system improved feedwater quality by reducing turbidity from over 10 NTU to less than 0.1 NTU, safeguarding downstream RO membranes and drastically decreasing maintenance downtime.
Technical Principles and Key Components

An industrial ultrafiltration system operates on the principle of pressure-driven membrane separation. Feed water passes through hollow fiber or flat-sheet polymer membranes under controlled pressure. The membranes selectively allow water molecules and low-molecular-weight solutes to pass while rejecting larger particles, colloids, bacteria, and some viruses.
Key components include:
- Membrane Modules: Constructed from advanced polymers such as polysulfone or PVDF for chemical and thermal resistance.
- High-Precision Pumps: Ensure steady operating pressure, essential for consistent filtration performance.
- Automated Control Systems: Feature SCADA or PLC controls for real-time monitoring of parameters like pressure, flow rate, turbidity, and membrane integrity.
- Backwash and Cleaning Mechanisms: Automated chemical cleaning cycles reduce fouling and extend membrane lifespan.
- Pretreatment Filters: Sand, carbon, and softener filters to protect membranes from abrasion, chlorine, and scaling.
Implementing these technologies ensures compliance with updated water quality standards such as the EN ISO 7704:2023 framework, which mandates rigorous performance testing of membrane filtration systems integrated with microbiological assessment.
From my observations on pharmaceutical sector projects, sophisticated automation and membrane cleaning protocols improved membrane uptime by approximately 30%, yielding consistent ultrapure water production essential for cGMP standards.
Price Structure: Investment and Operation Costs Breakdown
Assessing the cost of an industrial ultrafiltration system goes beyond the initial capital expenditure. Price components typically include:
- Base System Price: Cost of membranes, frame assemblies, pumps, and control units.
- Pretreatment & Post-treatment Modules: Additional filters and chemical dosing units.
- Installation & Commissioning: Site preparation, piping, electrical works, and system start-up.
- Operation & Maintenance: Consumables such as chemicals for cleaning, membrane replacement schedule, and energy consumption.
The complexity of feed water chemistry and volume requirements heavily influence total costs. Systems treating highly contaminated or variable water quality tend to be more expensive due to additional pretreatment needs and frequent maintenance. A recent study summarizes that flow rate and contaminant characteristics are the most significant cost drivers for industrial water treatment setups (cost determinants).
For example, on a mining site project I consulted, the upfront investment reached $350,000 for a 50 m3/h ultrafiltration system, with annual operational costs approximating 12% of the capital, primarily attributed to maintenance labor and cleaning chemicals. The return on investment was realized within three years due to water reuse savings and reduced environmental discharge penalties.
Performance Specifications and Quality Assurance
Industrial ultrafiltration systems must meet rigorous performance benchmarks for reliability and water quality. Typical specifications include:
| Parameter | Typical Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Removal Rate (Turbidity) | >99% | Achieves turbidity < 0.1 NTU |
| Bacterial Removal | >99.9% | Ensures microbiological safety |
| Operating Pressure | 0.2 – 0.5 MPa | Optimal membrane performance |
| Flux Rate | 30 – 70 L/m²·h | Depends on feedwater quality |
Quality control processes involve stringent membrane manufacturing standards and testing protocols, aligned with certifications such as UL’s water filtration certification programs. These programs guarantee membrane durability, safety, and functional compliance, critical for industrial users focused on consistent output and regulatory adherence.
Market and Application Scenarios Analysis
Industries face unique water quality challenges depending on geographic and operational contexts. For example, in Southeast Asia’s humid climates, river water often carries high turbidity and microbial loads, necessitating robust pretreatment integrated with ultrafiltration. In arid regions, groundwater sources might contain elevated dissolved solids alongside particulates.
The ultrafiltration system adapts well to these varying conditions, offering reliable particulate removal without affecting dissolved salts, thus preserving component integrity for downstream processes like reverse osmosis or ion exchange. This flexibility supports sustainable practices by reducing freshwater consumption and wastewater discharge impact, supporting the goals outlined in studies highlighting environmental sustainability of water treatment.
From operational data in South American food factories, ultrafiltration reduced microbial load by up to 99.95%, boosting production line hygiene and extending shelf life without additional preservatives.
Practical Case Studies: Real-World Performance Insights
My team recently oversaw the implementation of a complete water treatment line including an ultrafiltration stage for a medium-scale bottled water producer in Africa. The system treated 40 m3/day of well water with significant particulate matter and fluctuating microbial content. Results included:
- Turbidity reduction from 25 NTU to below 0.1 NTU consistently.
- Stable transmembrane pressure readings indicating low fouling rates.
- Membrane life extension over three years versus previous systems averaging 18–24 months.
- Compliance with local and international microbial safety standards.
These improvements translated into operational cost savings of approximately 15% yearly and enhanced product quality, affirming the strategic value of investing in a robust ultrafiltration system.
Customized Solutions and Comprehensive After-Sales Support
Every industrial water treatment setting demands tailored solutions. Ultrafiltration system configurations can include options such as:
- Feedwater pretreatment with multi-media filters and softeners to reduce membrane fouling.
- Post-treatment UV sterilization or chemical dosing to meet specific hygiene requirements.
- Automation upgrades for remote operation and predictive maintenance capabilities.
- Modular expansion possibilities for future capacity upgrades.
The holistic approach extends beyond equipment supply, encompassing installation, operator training, routine inspection, and membrane replacement programs to maximize system longevity and performance consistency.
One important practice I follow is integrating condition-based maintenance protocols enabled by real-time sensor data — reducing unexpected downtime and optimizing cleaning schedules, indispensable for industrial clients requiring maximal uptime.
Manufacturer Profile and Partnership Advantages
A leading global manufacturer with over 14 years of industry experience offers a diverse portfolio including industrial ultrafiltration, reverse osmosis, nanofiltration, and desalination systems. Operating from two standardized production facilities over 10,000 square meters, their capability covers comprehensive solutions incorporating spare parts such as filter cartridges, UV systems, FRP tanks, and filling equipment, trusted globally.
Their philosophy emphasizes quality, environmental responsibility, and customer-centric service — supported by a vast client base spanning Southeast Asia, Africa, and South America. This manufacturer’s dedication to continuous innovation and rigorous quality assurance aligns with global certification standards and sustainability goals.
As Mrs. Carrie Chan, the owner, articulates: “We hope everyone in the world can drink clean and pure water produced by our Reverse Osmosis Water treatment system, and we’ll try our best to take the responsibility of protecting our environment.”
Comprehensive Conclusion and Investment Recommendations
To summarize, deploying a state-of-the-art industrial ultrafiltration system translates into tangible operational gains—superior water quality, reduced maintenance costs, environmental compliance, and flexible scalability. My consultancy has repeatedly demonstrated that pairing ultrafiltration with tailored pretreatment and automation significantly enhances process efficiency and product consistency.
When considering investment, enterprises should account holistically for upfront equipment costs plus lifecycle expenses, aligned with specific feedwater conditions and capacity needs. Prioritizing manufacturers with recognized certification credentials and after-sales service infrastructure maximizes return on investment.
In the context of evolving industrial water quality regulations and environmental stewardship, ultrafiltration offers a sustainable, high-performance platform adaptable to diverse applications, helping your plant remain competitive while safeguarding natural resources.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the main benefit of using an industrial ultrafiltration system?
Ultrafiltration effectively removes suspended solids, bacteria, and colloids, ensuring high-quality water that protects downstream equipment and meets regulatory standards.
Q2: How does ultrafiltration differ from reverse osmosis?
Ultrafiltration retains larger particles and microorganisms but allows dissolved salts to pass; reverse osmosis removes dissolved salts and smaller molecules, providing higher purity water.
Q3: What industries commonly use industrial ultrafiltration systems?
Industries include mining, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics manufacturing, municipal water treatment, and laboratories.
Q4: What are typical operating pressures for ultrafiltration membranes?
Operating pressures range from 0.2 to 0.5 MPa depending on system design and feed water quality.
Q5: How long do ultrafiltration membranes typically last?
With proper maintenance and cleaning protocols, membranes can last 3 to 5 years, though this varies based on feed water conditions.
Q6: Is pretreatment necessary before ultrafiltration?
Yes, pretreatment like sand or carbon filtration protects membranes from fouling and extends their lifespan.
Q7: Can ultrafiltration systems be automated?
Modern ultrafiltration systems often include automated control and monitoring for efficient operation and maintenance planning.
Q8: What environmental benefits do ultrafiltration systems provide?
They reduce the need for chemical additives, decrease wastewater contamination, and enable water reuse, supporting sustainable water management.
Q9: How much does an industrial ultrafiltration system cost?
Costs vary widely based on capacity, feed water quality, and system complexity, ranging from tens of thousands to several hundred thousand dollars.
Q10: What certifications ensure ultrafiltration system quality?
Certifications from organizations like UL and compliance with standards such as EN ISO 7704:2023 ensure product safety and performance.