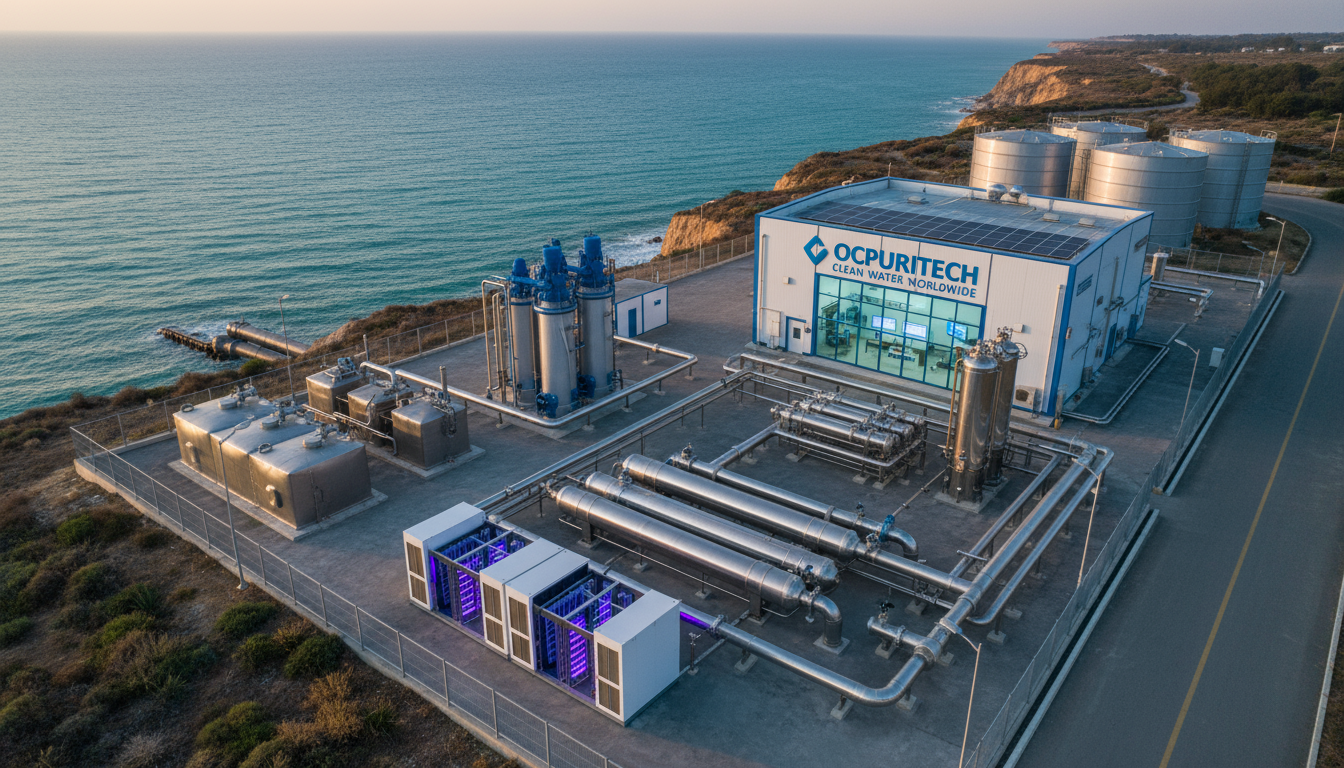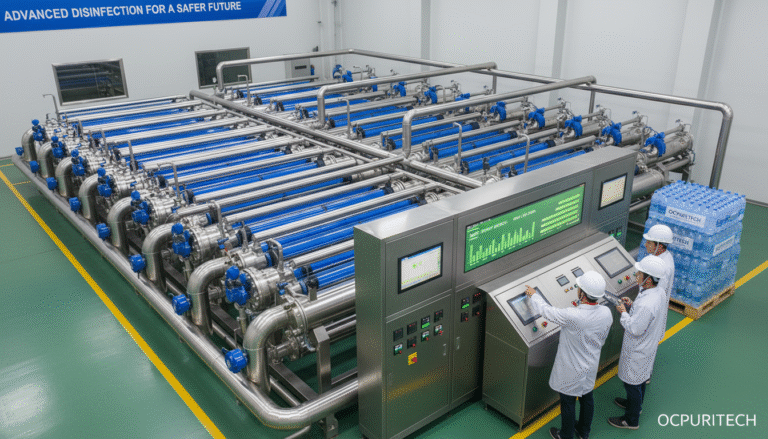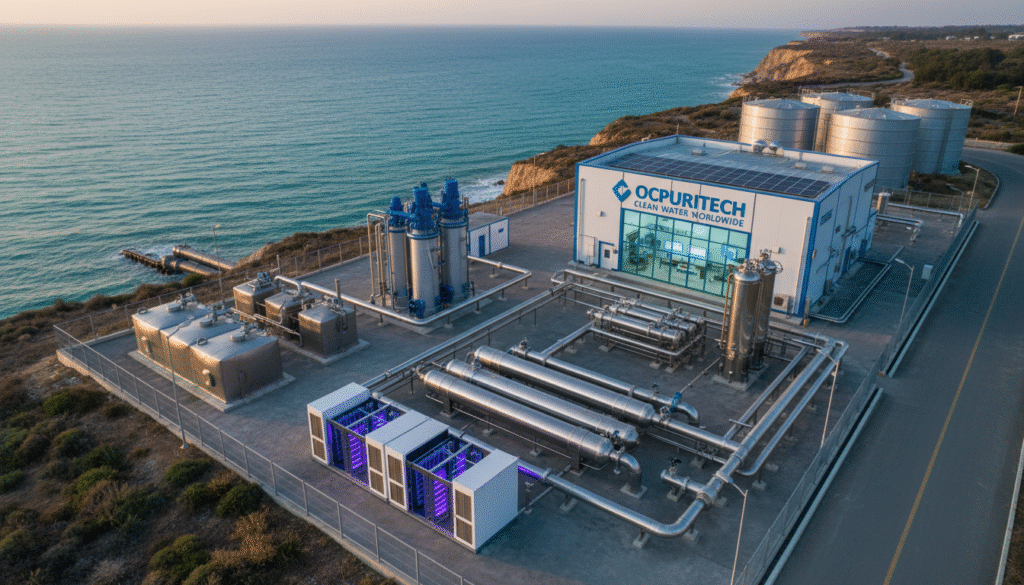
In the industrial and commercial sectors, water quality directly impacts operational efficiency, product quality, and environmental compliance. Innovations in ozonation water treatment systems play a pivotal role in optimizing process water by effectively eliminating contaminants, enhancing disinfection, and reducing chemical usage. This article delves into the technical intricacies of such systems, highlighting how different equipment modules accommodate varying output capacities and industrial demands while offering robust solutions for water purification challenges.
Advanced Reverse Osmosis Membrane Systems in Industrial Water Treatment

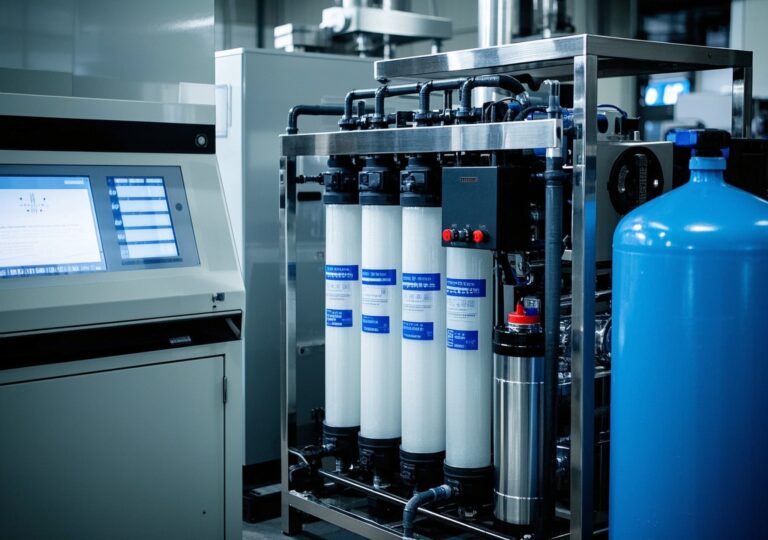
Reverse osmosis (RO) membrane technology remains foundational in industrial water treatment, serving as the primary mechanism for removing dissolved salts, organics, and particulate matter. Typically, RO systems are categorized by output: small-scale units producing under 10 m³/h, mid-size systems ranging from 10 to 50 m³/h, and large-scale configurations exceeding 50 m³/h for heavy-duty applications like seawater desalination.
Each system incorporates multi-stage filtration steps, beginning with sand and carbon filters to reduce turbidity and organic load. The core RO membranes then enable high salt rejection rates above 98%, which safeguards downstream equipment and processes.
In my operational experience with a brackish water RO system deployed in a food and beverage plant, integrating an ozone treatment stage upstream notably extended the membrane life by mitigating biofouling. The plant consistently achieved permeate water with conductivity under 30 μS/cm and turbidity below 0.2 NTU, meeting stringent quality standards with reduced chemical cleaning frequency.
Such RO installations align closely with ISO standards for seawater reverse osmosis desalination, reinforcing best practice for membrane performance and process reliability.
Integrated Filtration and Softening Systems for Pretreatment

Pretreatment is critical for protecting RO membranes and ensuring consistent water quality. Filtration systems combining sand filters, activated carbon filters, and water softeners are extensively used to remove suspended solids, chlorine, and hardness-causing ions such as calcium and magnesium.
Equipment configurations vary from compact units suitable for small commercial needs to scalable assemblies accommodating industrial flow rates exceeding 100 m³/h. Automated backwash and regeneration cycles optimize system uptime and reduce manual intervention.
From my observations working with pharmaceutical production facilities, employing a carefully tuned softening system reduced scaling risk in RO elements by over 70%, leading to substantial savings in maintenance costs and downtime.
Pretreatment practices adhere to recommendations such as those detailed in UV disinfection guidelines by the UK Drinking Water Inspectorate, which stress the importance of turbidity control below 0.2 NTU for microbial safety.
Containerized Ozonation Water Treatment Systems: Efficiency and Mobility

The rise of containerized water treatment units revolutionizes how industries access, deploy, and maintain purification infrastructure. These systems encapsulate ozonation, filtration, and disinfection technologies within weather-resistant shipping containers, permitting rapid installation and relocation.
Ozone, a powerful oxidant, effectively degrades organic pollutants, disinfects pathogens, and reduces biofilm formation on membranes and pipes. Integrating ozonation with monitoring controls optimizes operational parameters to balance performance with energy consumption.
In a recent project supporting a remote mining operation, our containerized ozonation system delivered 25 m³/h of high-quality process water with total organic carbon (TOC) reduced by over 60%, enabling consistent production despite challenging source water variability.
Containerized plants correspond well with contemporary trends highlighted by industry experts advocating modular and mobile solutions for variable industrial scenarios, as discussed in containerized water treatment innovations and Veolia’s insights on containerized water treatment.
UV Sterilization and Ozonation Synergy for Enhanced Disinfection

Ultraviolet (UV) irradiation is a well-established disinfection method that inactivates microorganisms by disrupting their DNA. When combined with ozonation, the synergy enhances treatment efficacy, tackling resistant pathogens and reducing disinfection byproducts.
These systems typically categorize UV units into Class A or Class B based on delivered UV dose, per NSF/ANSI 55-2024 standards. Maintaining low turbidity under 0.2 NTU is critical to ensure UV light penetration and maximize microbial inactivation.
I have witnessed the implementation of combined ozone/UV treatment in coastal seawater desalination plants. The dual process significantly improves microbiological safety and reduces chemical disinfectant residues to negligible levels, meeting international guidelines on drinking water reuse outlined in NWRI’s UV disinfection guidelines.
Key Takeaways and Practical Implementation Insights
- Utilizing modular RO systems with integrated pretreatment ensures scalable and resilient water purification for diverse industrial requirements.
- Containerized ozonation units enable flexible deployment in remote or dynamic settings while ensuring high disinfection performance and reduced chemical usage.
- Combining UV sterilization with ozonation offers advanced microbial control, meeting or exceeding rigorous international standards for water reuse and drinking water safety.
- Adherence to ISO and ANSI standards guarantees system reliability and process water quality, supporting regulatory compliance and sustainable operations.
At Ocpuritech, we specialize in delivering such integrated solutions backed by over a decade of experience and manufacturing excellence. Our portfolio ranges from compact household units to expansive industrial systems, including Remote Control Reverse Osmosis, Brackish Water RO, Sea Water Desalination, Ultrafiltration, Nanofiltration, and EDI technologies. Supported by our large-scale production facilities in Guangzhou and Jiangmen, we ensure cost-effective, high-quality purification equipment tailored to global markets including Southeast Asia, Africa, and South America.
Our mission, inspired by the company founder Mrs. Carrie Chan, is to empower industries worldwide to access clean and pure water through advanced Reverse Osmosis and ozonation water treatment systems, contributing actively to environmental sustainability.
FAQ
Q1: What are the main advantages of ozonation in industrial water treatment?
Ozonation effectively oxidizes organic pollutants, disinfects pathogens, reduces biofouling on membranes, and lowers the demand for chemical disinfectants, improving water quality and equipment lifespan.
Q2: How do containerized water treatment systems benefit remote industrial sites?
They provide mobility, rapid deployment, and integrate multiple processes such as filtration, ozonation, and UV disinfection within compact units, reducing installation time and operational complexity in challenging environments.
Q3: What is the typical output range for industrial reverse osmosis systems?
RO systems can be designed for small capacities below 10 m³/h, mid-range 10–50 m³/h, and large-scale above 50 m³/h, tailored to application needs from commercial to seawater desalination.
Q4: Why is pretreatment necessary before RO membranes?
Pretreatment through filtration and softening removes turbidity, chlorine, and hardness ions, preventing membrane fouling and scaling, thereby extending membrane life and stabilizing system operation.
Q5: How does UV disinfection complement ozonation?
UV light inactivates microorganisms by damaging their DNA, while ozonation breaks down organic matter and pathogens chemically; together, they provide superior microbial safety and reduce harmful byproducts.
Q6: What operational standards govern ozonation and UV water treatment?
International standards such as the ISO for RO systems, NSF/ANSI 55-2024 for UV treatment, and guidance from entities like the UK Drinking Water Inspectorate set performance and safety benchmarks.
Q7: Can ozonation systems reduce chemical cleaning in industrial water plants?
Yes, ozonation minimizes biofilm and microbial contamination, decreasing the frequency and volume of chemical cleaning required for membranes and piping.
Q8: What industries benefit most from advanced ozonation water treatment?
Food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, agriculture, mining, seawater desalination, and bottled water production all gain enhanced water quality and process efficiency from these treatments.
Q9: How does water turbidity affect UV disinfection?
High turbidity scatters and absorbs UV light, reducing disinfection efficacy; maintaining turbidity below 0.2 NTU is critical for optimal UV system performance.
Q10: What is the environmental impact of using advanced ozonation systems?
They reduce the need for hazardous chemicals, improve water reuse potential, and help industries meet sustainability goals by providing cleaner process water with minimal environmental footprint.