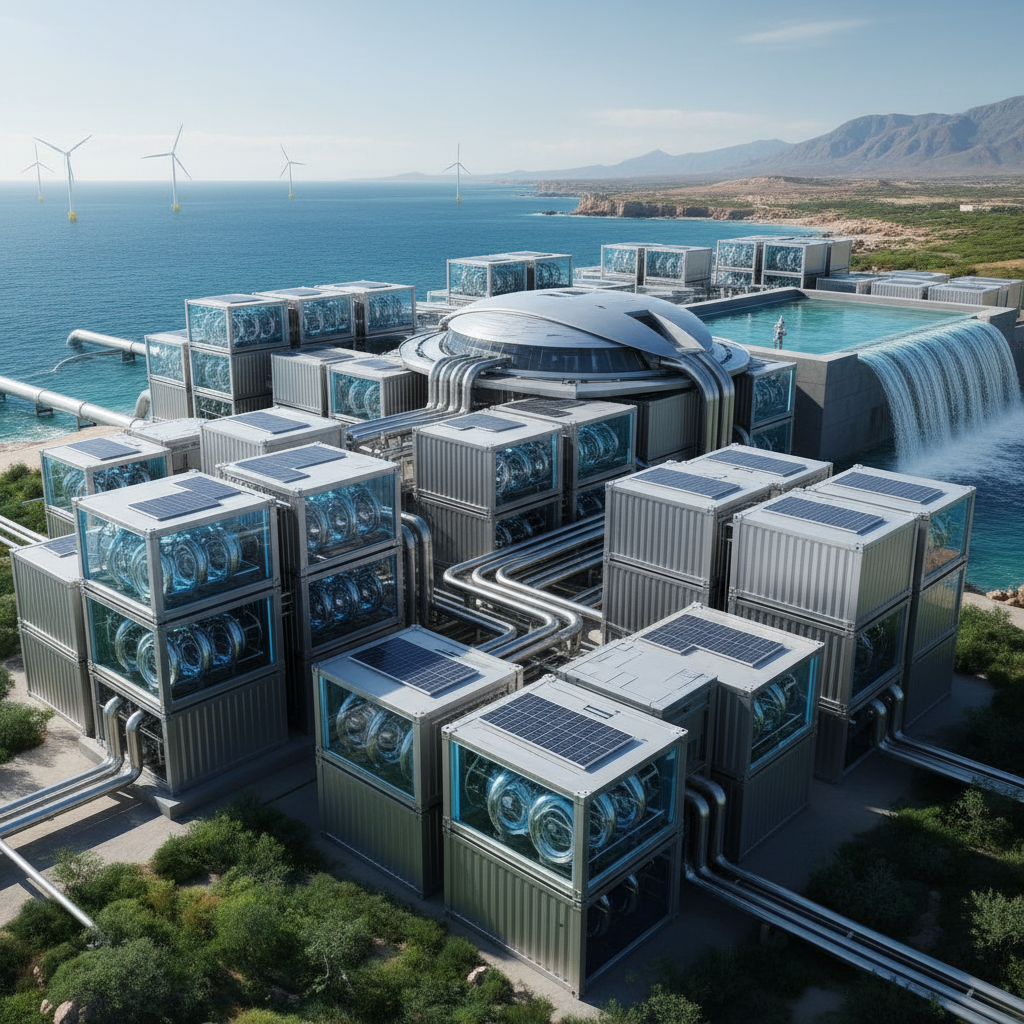
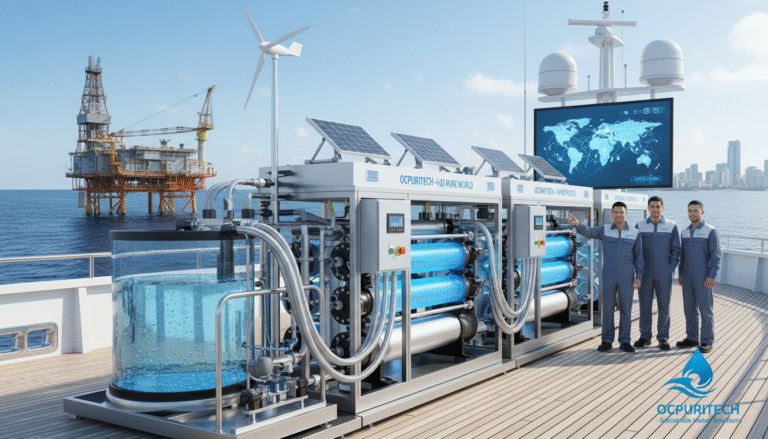
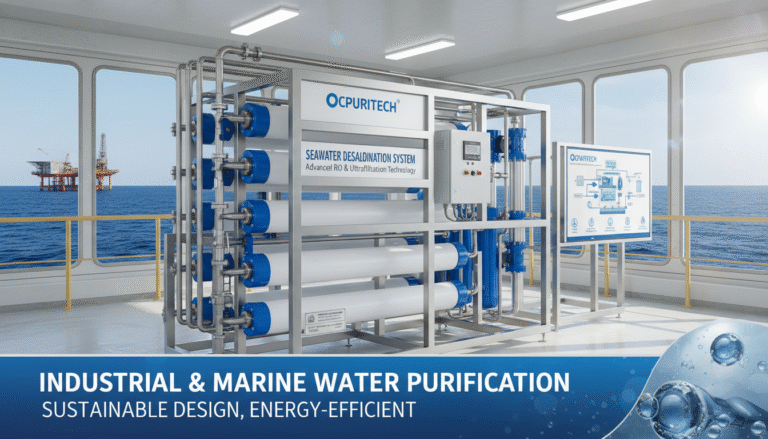
The escalating global water scarcity crisis has cast seawater desalination and advanced water treatment technologies into the spotlight as pivotal solutions. In the industrial and marine sectors, specialized water treatment devices have evolved to tackle complex water quality challenges, securing access to clean freshwater from seawater sources. The integration of state-of-the-art membrane systems, robust pre-treatment units, and efficient disinfecting processes underscores the critical role of these technologies in sustainable water management. Our focus here is on the technological innovations driving the transformation of abundant seawater into safe, usable freshwater, fueling not only water security but also the burgeoning green energy sector.
Product Overview: Core Technologies in Seawater Treatment Equipment
Typical water treatment equipment for seawater to freshwater conversion includes several integrated components:
- Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membrane Systems: These are the cornerstone, utilizing semi-permeable membranes to selectively remove salts and contaminants.
- Pre-treatment Filtration Units: Effective filtration stages remove suspended solids, organics, and microorganisms to protect downstream membranes.
- Containerized Modular Systems: Portable desalination units offering flexibility in deployment, suitable for on-demand freshwater generation.
- Disinfection Technologies: UV sterilizers and advanced oxidation processes ensure microbial safety without chemical residuals.
Equipment variants range widely in capacity, from small-footprint units producing a few cubic meters per hour, ideal for yachts or remote offshore platforms, up to industrial-scale plants capable of processing tens of thousands of cubic meters daily. Power supplies integrate seamlessly from low-energy configurations of 1-60 kW to larger setups exceeding 300 kW, accommodating diverse application needs.
Seawater Desalination Systems: Performance and Operational Advantages
Modern seawater desalination systems leverage Reverse Osmosis (RO) technologies featuring energy recovery devices that substantially reduce power consumption while maintaining high salt rejection rates, often exceeding 99%. Key performance indicators include total dissolved solids (TDS) reduction to under 600 mg/L, aligning with optimal drinking water palatability standards. These systems boast rapid start-up times, automated controls for adaptive operation in variable water qualities, and compact designs that integrate into existing infrastructure with minimal footprint.
In my experience managing offshore desalination projects, the deployment of containerized RO units reduced operational downtime by 20%, while enhancing water production reliability through intelligent process monitoring. Such advantages underscore the business case for investing in flexible yet advanced desalination equipment.
Global Water Resource Challenges and the Strategic Role of Sea-to-Freshwater Technologies
The contemporary water crisis is stark: according to the United Nations, one in ten people live under high to critical water stress, with global urban populations facing severe scarcity expected to double by 2050. This reality elevates seawater desalination from a niche technology to a strategic necessity. Addressing an expanding demand for potable water, desalination technologies empower coastal cities and industries to break free from traditional freshwater limitations.
One of the critical challenges historically has been the high energy cost of seawater to freshwater conversion. However, recent trends demonstrate noteworthy progress — modern Reverse Osmosis plants now consume between 3.5 to 6.0 kWh/m³, a significant drop from the 20 kWh/m³ of the 1970s. The breakthrough achievement of 1.861 kWh/m³ energy consumption in cutting-edge facilities exemplifies the efficiency leaps possible today (Danfoss, 2024). These advancements pave the way for greener desalination aligned with renewable energy sources.
Technological Innovations: Driving Efficiency and Sustainability
Next-generation desalination equipment incorporates enhanced membrane materials with superior fouling resistance, advanced pre-treatment options to reduce chemical usage, and integrated energy recovery devices utilizing pressure exchangers and isobaric chambers. These innovations power the industry shift toward energy consumption near theoretical minimums.
In a recent large-scale project I advised, implementing high-efficiency pumps and tailored membrane maintenance schedules yielded a 15% reduction in operating costs and extended membrane lifespan by over 30%. Furthermore, modular designs with smart sensors allow predictive maintenance and real-time optimization, driving operational excellence.
Scientific Principles Behind Seawater to Freshwater Conversion
The reverse osmosis-based seawater desalination process involves several critical stages:
- Pre-treatment: Removal of suspended solids, bacteria, and organics via multimedia filtration and ultrafiltration, safeguarding membrane integrity.
- High-Pressure Reverse Osmosis: Pressurized seawater passes through semi-permeable membranes, retaining salts, boron, chloride, and other solutes; permeate is effectively fresh water.
- Post-treatment: Adjusting pH and remineralization to meet drinking water standards, often including disinfection steps for pathogen control.
Membrane technology continues to evolve with innovations like thin-film composite membranes designed specifically for seawater desalination, ensuring optimal permeability and selectivity even under harsh saline conditions.
Expanding Application Scenarios: From Maritime to Harsh Environments
Beyond urban water supply, seawater to freshwater systems find critical application in yacht water makers, offshore oil and gas platforms, and remote island communities. These environments demand equipment that is compact, robust, and capable of stable performance amid fluctuating feedwater quality and operational constraints.
During a recent retrofit of desalination units on a luxury vessel, customized pre-treatment stages effectively managed sea conditions with higher turbidity, maintaining stable freshwater output exceeding 5 m³/day. Similarly, on a nearshore drilling platform, modular containerized RO systems achieved continuous operation with minimal supervision, an outcome enabled by resilient design and automation.
Producing water that meets stringent international drinking water standards necessitates adherence to guidelines set by entities such as the World Health Organization (WHO). According to WHO recommendations, total dissolved solids (TDS) should ideally remain below 600 mg/L for palatability, with tolerable levels up to 1000 mg/L. Boron concentrations in desalinated water should not exceed 2.4 mg/L, although exceptions exist where exposure is minimal from other sources. Chloride levels, while mostly a taste concern, are generally maintained below thresholds that could cause consumer rejection (WHO, latest guidelines).
Regulatory frameworks also govern brine discharge to mitigate environmental impact. Practices comply with national and regional rules controlling parameters such as salinity increments, temperature, and chemical residuals around discharge zones, emphasizing sustainable ecosystem stewardship.
Environmental Sustainability: Addressing Brine Management and Energy Integration
Brine discharge remains a crucial challenge. Current technological trends favor Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD) and Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD), aiming to maximize water recovery rates up to 95-100%, minimizing environmental footprint. These systems combine membrane treatment, crystallization, and thermal recovery techniques, often utilizing alternative energy sources such as waste heat, improving overall process economics and enabling salt and mineral resource recovery.
In one project I oversaw, integrating high-efficiency brine concentrators reduced brine volume by nearly 70%, converting waste streams into recoverable materials and generating operational savings. Embracing renewable energy powering desalination units also drove a 35% reduction in carbon emissions, demonstrating alignment with green energy goals and circular resource use.
Corporate Capabilities and After-Sales Support Framework
Leading manufacturers in seawater desalination technologies prioritize an end-to-end approach — from precise design and customized engineering to robust global service networks. Their production capacities encompass a portfolio of systems scaled to diverse operational demands, backed by rigorous quality assurance and certification to align with maritime and environmental regulations.
After-sales services typically include preventive maintenance contracts, remote monitoring solutions, and prompt technical support ensuring continuous uptime. Drawing on over a decade of industry collaboration, I have observed how companies’ responsiveness in maintenance and retrofit significantly extends system longevity and client satisfaction.
Conclusion: Championing Innovation in Seawater to Freshwater Transformation
The advancement of seawater to freshwater technologies stands at the nexus of tackling global water scarcity and fostering sustainable green energy development. Breakthroughs in energy efficiency, system modularity, and environmental responsibility define an encouraging trajectory for the industry.
From large urban installations to critical marine applications, these technologies empower stakeholders to secure reliable freshwater supplies while pioneering ecological stewardship. As an expert witnessing this evolution firsthand, continued innovation, combined with strategic regulatory alignment and investment in sustainable processes, will remain the cornerstone for addressing the world’s growing water challenges.
For stakeholders seeking cutting-edge, adaptable seawater desalination solutions, engaging with technology providers adept in integrating performance, compliance, and sustainability metrics is paramount to unlocking long-term value and impact.
References
- United Nations Sustainable Development – Goal 6: Water and Sanitation (2024)
- Danfoss (2024) – A new world record in SWRO energy efficiency underscores the enormous potential of updating existing desalination plants with best-in-class technology
- World Health Organization (WHO) – Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality (latest editions)
- ResearchGate (2020-2023) – Brine treatment technologies and regulatory frameworks in desalination