Ensuring clean, safe water is a cornerstone for many industries worldwide, especially in regions facing significant water contamination challenges. A reliable membrane ultrafiltration system offers an effective solution for removing suspended solids, pathogens, and certain chemical contaminants to provide high-quality water for industrial and municipal needs. This article explores the technology behind these systems, their application across various industries, pricing elements, and practical experience from the field.
Product Overview: Versatile Ultrafiltration Solutions for Diverse Industries

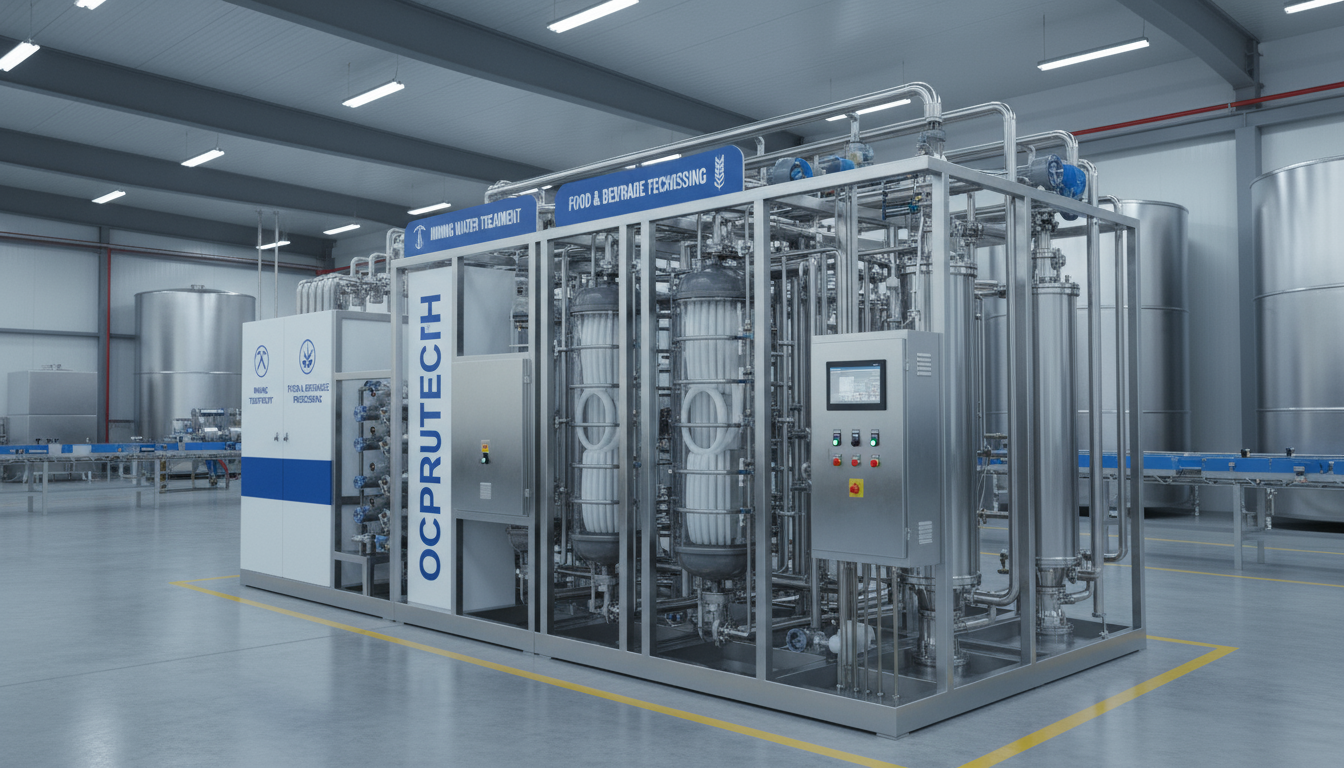
Membrane ultrafiltration systems leverage thin semipermeable membranes to physically separate contaminants from water. They effectively remove suspended particles, bacteria, viruses, and some larger organic molecules while allowing water and low molecular weight solutes to pass through. Such systems serve a wide array of industries, including mining, food and beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, agriculture, municipal water supplies, and boiler feedwater treatment.
For instance, in mining, ultrafiltration helps manage process water reuse by filtering out sediments and microbes, reducing environmental discharge. The food industry relies on ultrafiltration for clarifying fruit juices and purifying process water without chemicals. In pharmaceutical and cosmetic production, water quality standards require microbe-free water; ultrafiltration fits as a critical barrier stage before further purification.
Water sources range from city supply and groundwater to river water and seawater desalination feedwater. Membrane ultrafiltration systems tailored to these sources ensure adaptability to varying contaminant profiles, such as heavy metals and microbial loads prevalent in Southeast Asia, Africa, and South America, where arsenic and microbial contamination pose serious health risks (World Health Organization and UNICEF data).
Technical Principles and Key Components


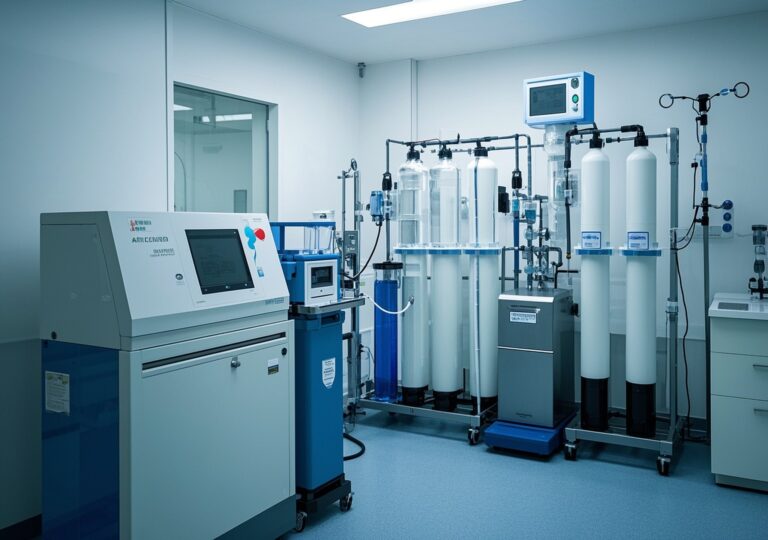
The core of an ultrafiltration system is its membrane module, typically composed of hollow fiber or spiral wound membranes with pore sizes ranging from 0.01 to 0.1 microns. These membranes function as physical barriers that reject bacteria, suspended solids, endotoxins, and larger organic molecules while allowing water and dissolved salts to permeate. This rejection efficacy supports compliance with stringent pharmaceutical and cosmetic water standards, such as USP and European Pharmacopoeia requirements.
Automated control systems are an integral part of modern ultrafiltration units, enabling real-time monitoring of parameters like transmembrane pressure, turbidity, and flow rates. Automation ensures optimal performance, early detection of membrane fouling, and efficient chemical cleaning cycles, reducing downtime and operational costs.
Pretreatment stages, including sand filters, carbon filters, and water softeners, often precede ultrafiltration to protect membranes from large particulates and scale-inducing ions. This layered approach extends membrane life and stabilizes system performance, which is especially crucial in treating hard water that otherwise leads to scaling and energy penalties up to 20% in industrial boiler operations (U.S. Department of Energy findings).
Price Breakdown: Understanding Investment and Operating Costs
The investment in a reliable membrane ultrafiltration system combines initial capital costs with ongoing operational expenditures. Understanding these components is vital for planning and maximizing return on investment.
- System Hardware: Includes membrane modules, skid frames, pumps, valves, and automated instrumentation. Membrane modules often represent the largest portion of this expense.
- Pretreatment and Post-treatment Modules: Sand filters, carbon filters, UV sterilizers, or chemical dosing systems may be required depending on feedwater quality.
- Installation and Commissioning: Labor, piping, electrical work, and integration add to upfront costs.
- Maintenance and Consumables: Membrane cleaning chemicals, replacement modules, and energy consumption over the system lifetime.
From my experience managing water projects, initial system costs may range widely from tens of thousands to several hundred thousand dollars depending on capacity and customization. However, properly designed systems can reduce maintenance-related shutdowns by up to 40% and prolong equipment lifespan by about 50%, generating significant savings over time (industry insights from Indian boiler water treatment cases).
Performance Specifications and Quality Assurance
Key performance indicators for ultrafiltration systems include:
| Parameter | Typical Range / Value | Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Flux Rate | 50-100 L/m²/h | Indicator of water throughput per membrane area |
| Membrane Rejection | >99% Bacteria, >90% Viruses | Ensures microbial safety |
| Operating Pressure | 1.5-5 bar | Affects energy consumption and membrane life |
| Membrane Material | Polyethersulfone (PES), Polysulfone (PS) | Chemical and temperature resistance |
Quality assurance extends from membrane manufacturing compliance to factory acceptance testing and field performance monitoring. Brands with certifications aligned with NSF, FDA, and relevant pharmacopoeia standards provide added reliability and traceability.
Market and Application Scenario Analysis

Globally, industrial water treatment markets are booming with anticipated growth CAGR of 5.1% through 2033, driven primarily by Asia-Pacific regions which hold 38% market share and experience more than 6% CAGR growth (Grand View Research data). This growth aligns with expanding industrial activities needing better water quality for manufacturing and environmental compliance.
In regions like Southeast Asia and South America, water sources are often challenged by heavy metals such as arsenic, mercury, and lead, alongside microbial contamination. The presence of high Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) or salinity particularly in groundwater requires pre-treatment combined with membrane ultrafiltration. Projects I have been involved within the Indo-Gangetic Basin region illustrate how integrating ultrafiltration has reduced unsuitable water usage by over 70% in affected plants.
Key industries benefiting from ultrafiltration include:
- Chemical manufacturing – accounts for over 28% of market revenue due to stringent purity requirements
- Electronics and semiconductor fabrication – demanding ultrapure waters with low TOC and microbial counts
- Food and beverage processing – requiring pathogen-free water for product consistency and safety
- Pharmaceutical and cosmetics production – needing compliance with GMP and pharmacopoeial standards
Case Insights: Practical Success from Field Deployments
In my role overseeing water treatment for a pharmaceutical manufacturer in Southeast Asia, deploying a high-quality reliable membrane ultrafiltration system drastically cut microbial counts and endotoxin levels within the purified water network. Our monitoring found endotoxin levels dropped below 0.1 EU/mL, well under USP limits. The system’s automated cleaning and monitoring significantly reduced manual sampling labor by 50%, improving operational efficiency.
Another important project involved an agricultural processing plant near the Indo-Gangetic Basin, where groundwater contained elevated arsenic and salinity. Combining ultrafiltration with prior softening and carbon filtration created a robust multi-barrier treatment. The plant reported a 60% reduction in water-related equipment malfunctions and a 20% energy saving attributed to cleaner feed water for boilers.
Such examples underscore that a reliable membrane ultrafiltration system not only enhances water quality but also extends the longevity and efficiency of downstream equipment, providing tangible economic benefits.
Customized Solutions and Comprehensive Service Support
A standout feature of effective ultrafiltration solutions is customization. Pretreatment designs tailored to incoming water quality ensure membrane longevity. For instance, integrating sand filters and automated backwash systems prevents rapid fouling. Post-treatment steps, such as UV sterilizers or ozonation, can provide additional biological safety depending on end-use needs.
Reliable providers offer turnkey services: system design, installation, commissioning, operator training, and maintenance contracts. Such support ensures consistent performance over the lifespan of the equipment. According to my observations in multiple industrial installations, continuous service reduces downtime by at least 35% and lowers unexpected repair costs.
Manufacturers’ Expertise and Competitive Advantages
Choosing suppliers with proven expertise and global certifications is paramount. Manufacturers like Ocpuritech, with two standardized factories in Guangzhou and Jiangmen and over 14 years of industry experience, deliver comprehensive solutions combining advanced membrane technologies and robust automation systems. Their product portfolio covers industrial to residential applications, fulfilling diverse purification demands.
The company’s focus on customer-centric innovation and environmental responsibility aligns with its vision “that everyone worldwide can enjoy clean and pure water, supported by sustainable water treatment technologies.” Their global case studies reflect successful deployments across Southeast Asia, Africa, and South America, meeting stringent quality and regulatory requirements.
Summary and Investment Guidance
A reliable membrane ultrafiltration system represents a strategic investment to safeguard water quality, reduce operational risks, and comply with increasingly strict industry standards. Key advantages include:
- High rejection of suspended solids and pathogens, ensuring safe process and potable water
- Modular design for easy scalability and integration into existing plants
- Automation features that cut labor and maintenance costs
- Compatibility with various pretreatment and post-treatment options to address specific water challenges
For industries targeting growth in emerging markets, particularly in areas with compromised water sources, ultrafiltration systems offer a robust pathway to improve water reliability and operational sustainability. Combining authoritative standards with practical field experience, choosing the right system supplier and customizing solutions to onsite conditions maximizes returns over the equipment lifecycle.
References to Authoritative Data
– World Health Organization (WHO), UNICEF, World Bank: Comprehensive Data on Water Contaminants and Water Quality Challenges
– Grand View Research: Industrial Water Treatment Market Projections
– U.S. Department of Energy: Impact of Water Hardness on Boiler Energy Consumption
– United States Pharmacopeia (USP), European Pharmacopoeia (EP), Chinese Pharmacopoeia (CP): Water Quality Standards for Pharmaceuticals
– European Cosmetics Regulation and FDA: Microbial and Pathogen Limits in Cosmetic Water Use